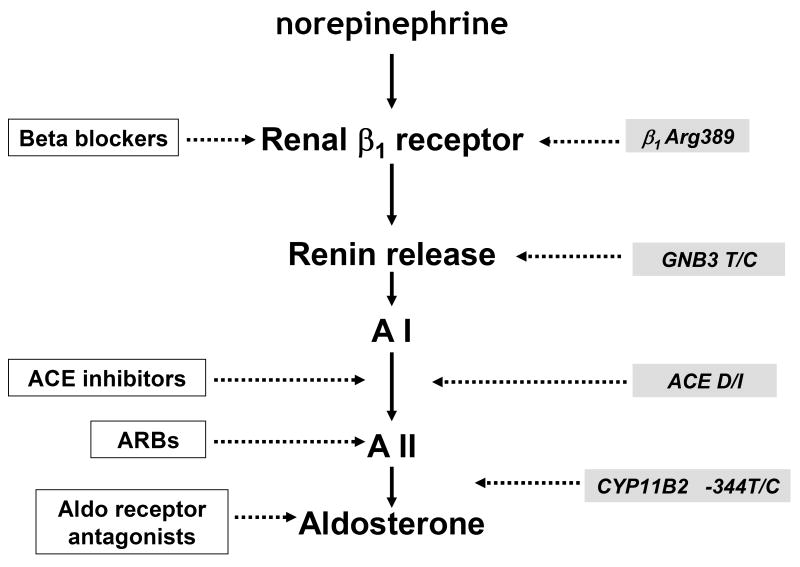
Figure 1. RAAS pathway and site of action of drug therapies and functional polymorphisms.
Major pharmacologic therapies which improve survival in heart failure in white boxes: beta blockers, ACE inhibitors, ARBs (angiotensin receptor blockers) and Aldo (aldosterone) receptor antagonists all act on RAAS. In grey boxes are major genetic polymorphisms which influence outcomes and the impact of therapy including β1Arg389, G protein β 3 subunit (GNB3 T haplotype linked to low plasma renin), ACE D/I (deletion/Insertion) and aldosterone synthase (CYP11B2) promoter