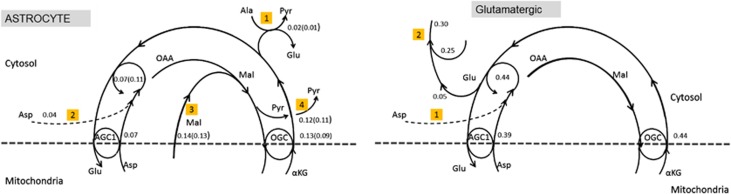
Figure 1.
Left: A schematics of the cytosol portion of the malate-aspartate shuttle (MAS) in astrocyte with the values of the mean reaction fluxes and transport rates in μmol/g per minute during awake steady state (AS). The flux values in parentheses refer to the case when there is no aspartate uptake from extracellular space (ECS). The imbalance between aspartate-glutamate carrier (AGC1)/aralar and oxoglutarate carrier (OGC) is compensated by the alanine-pyruvate shuttle (pathway 1), the optional aspartate uptake (pathway 2), and malate transport from mitochondria (pathway 3) and malic enzyme (pathway 4). Right: A schematics of the cytosol portion of the MAS in glutamatergic neurons with the values of the mean reaction fluxes and transport rates in μmol/g per minute during awake steady state (AS). The uptake of aspartate (pathway 1) replenishes the aspartate pool, balancing the aspartate-glutamate transaminase. The excess glutamate contributes to the neurotransmitter cycle (pathway 2), replenishing the pool originating from the glutamine-glutamate metabolism. αKG, α-ketoglutarate; OAA, oxaloacetate.