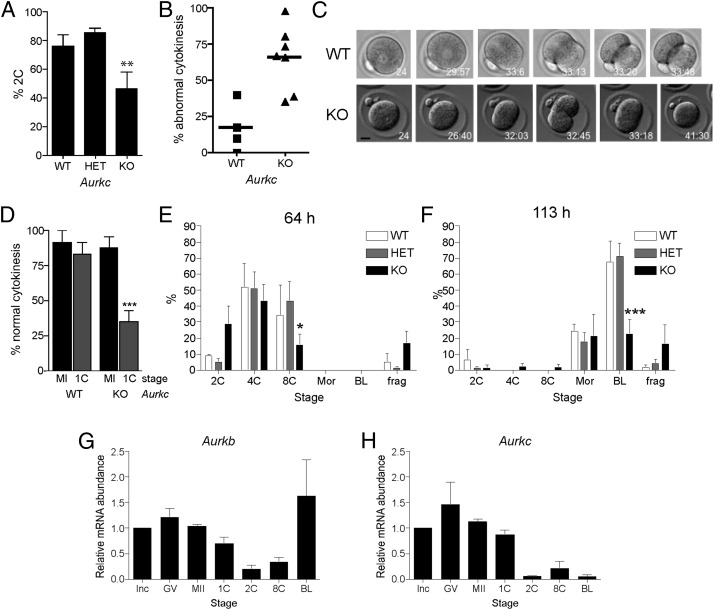
Fig. 2.
Embryonic development is compromised in Aurkc−/− mice. (A–F) Female mice of the indicated genotype were mated to wild-type males and one-cell embryos were isolated and cultured in vitro. (A) The percentage of one-cell embryos that cleaved to the two-cell embryonic stage. (B–D) Embryos were imaged live by DIC every 5–7 min. In B, the percentage of embryos with abnormal cytokinesis was plotted for each mouse. C contains representative images of a wild-type embryo undergoing normal cytokinesis (Upper) and a KO embryo failing cytokinesis (Lower). The time stamp is h:min after hCG injection. (Scale bar, 5 μm.) (D) The percentage of normal cytokinesis events from Fig. 1C (MI) and panel B (1C) were compared. (E and F) Embryo development was monitored at the indicated times after hCG and mating. These experiments were conducted four times with at least two mice per genotype each time, and the data are expressed as the mean ± SEM. (G and H) mRNA levels were measured by quantitative RT-PCR at the indicated stages. Data were normalized against a probe that detects exogenously added Gfp message. Mean (± SEM) from three independent experiments are shown. One-way ANOVA was used to analyze the data. *P < 0.05; **P < 0.01; ***P < 0.001. BL, blastocyst; frag, fragmented; GV, full grown GV-intact oocyte; Inc, meiotically incompetent oocyte; Mor, morula; 1C, one-cell embryo; 2C, two-cell embryo; 4C, four-cell embryo; 8C, eight-cell embryo.