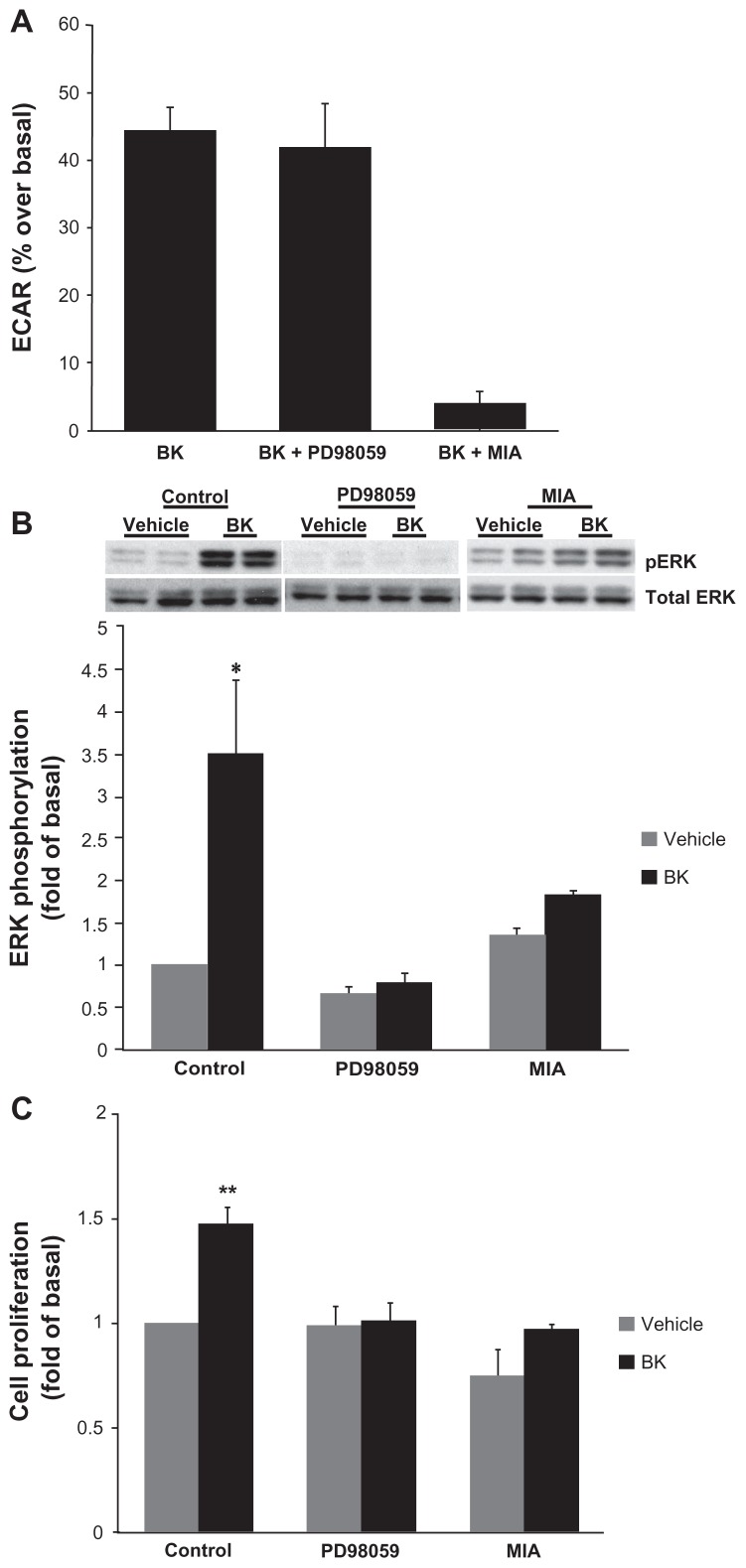
Figure 6.
NHE activity is required for bradykinin-induced ERK activation.
Notes: (A) BK-induced NHE activity does not require ERK activation. Cells were pretreated with either 10 μM of an MEK inhibitor (PD98059) or with 5 μM of an NHE inhibitor (MIA) for 30 minutes prior to the application of 100 nM of BK for four measurement cycles, and ECAR was assessed by proton microphysiometry as described in the Materials and methods section. Experiments were performed at least three times. The data are means + SEM. (B) BK-induced ERK phosphorylation is NHE-dependent. Cells were pretreated with 10 μM PD98059 or with 5 μM MIA for 30 minutes prior to stimulation with 100 nM BK for 5 minutes. Bars represent the intensities of phospho-ERK bands relative to the total ERK expressed as a fold of control (cells treated with a vehicle). Experiments were performed three times in duplicate. Data are presented as means + SEM. (C) Bradykinin stimulates the proliferation of A498 cells. A498 cells were preincubated for 1 hour with a vehicle, or with 10 μM PD98059 or 5 μM MIA before the addition of 100 nM BK or 20% fetal bovine serum (positive control) or a vehicle (negative control) for 24 hours. After incubation with a BrdU label for an additional 24 hours at 37°C, the BrdU cell proliferation assay was performed according to the manufacturer’s protocol. Experiments were performed at least three times in triplicate. Data are presented as means + SEM. Statistical probability in figures is expressed as *P < 0.05, and as **P < 0.01 versus vehicle-treated samples.
Abbreviations: BK, bradykinin; ECAR, extracellular acidification rate; ERK, extracellular signal-regulated kinase; MEK, mitogen- and extracellular signal-regulated kinase; MIA, 5-(N-methyl-N-isobutyl)-amiloride; NHE, Na+/H+ exchange; SEM, standard error of the mean.