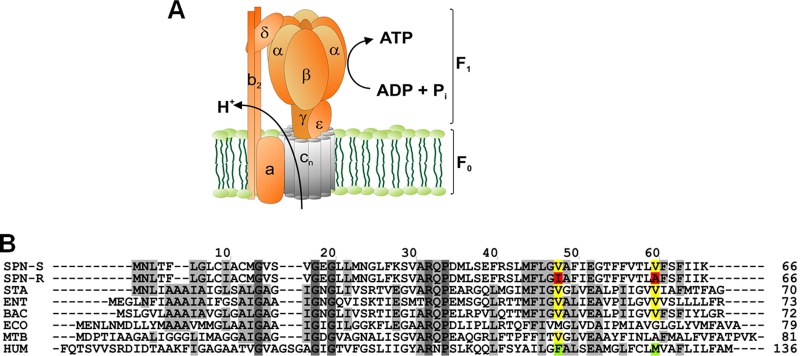
Fig 4.
ATP synthase and the proton-conducting subunit c. (A) Schematic view of ATP synthase subunits. The bacterial enzyme consists of a membrane-bound F0 part (subunits α3β3γδϵ) for conduction of protons, and a hydrophilic F1 part (subunits α3β3γδϵ) responsible for synthesis of ATP. The oligomeric subunit c (AtpE) is shown in gray. (B) Amino acid sequence alignment of ATP synthase subunit c for selected pathogens and human mitochondria. Species used: SPN_S, drug-sensitive strain of Streptococcus pneumoniae D39 (GenBank accession no. ABJ53659); SPN_R, drug-resistant strain of Streptococcus pneumoniae D39 (GenBank accession no. ABJ53659); STA, Staphylococcus aureus MRSA252 (residue 1 to 70; RefSeq accession no. YP_041556); ENT, Enterococcus faecalis V583 (residue 1 to 73; RefSeq accession no. NP_816252); BAC, Bacillus sp. PS3 (Swiss-Prot accession no. P00845); ECO, Escherichia coli (GenBank accession no. AAA24732); MTB, Mycobacterium tuberculosis (Gen Bank accession no. CCE36825); H. sapiens, Homo sapiens (residue 60 to 136; RefSeq accession no. NP_001002027). Single mutations found in drug-resistant S. pneumoniae (V48I and V60A) are indicated by boxes.