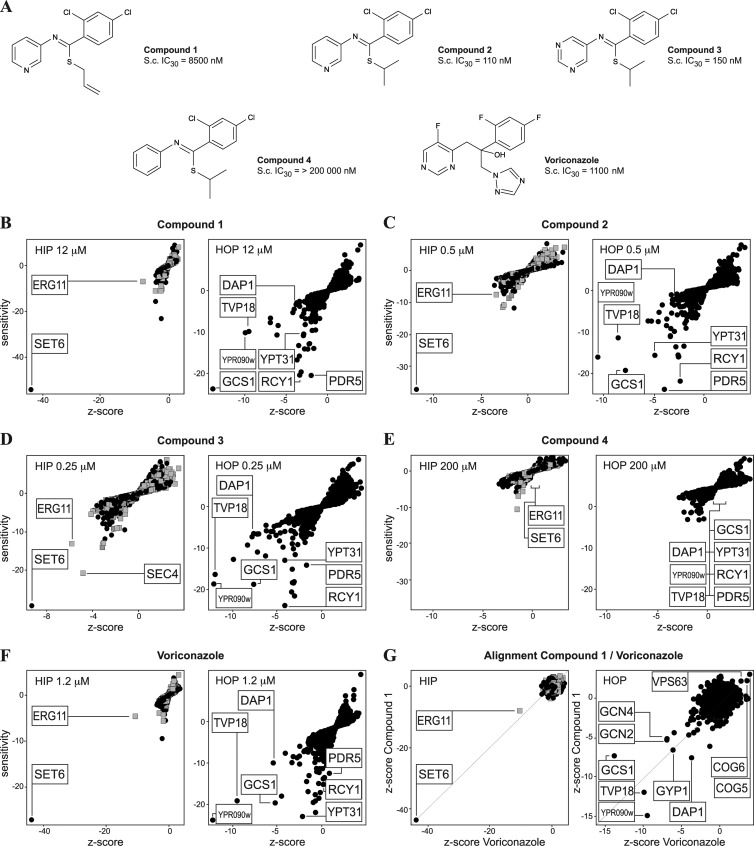
Fig 2.
HIP HOP profiling results. (A) Structures and S. cerevisiae (S.c.) IC30s of substances tested by HIP HOP profiling. (B to D) HIP HOP profiling of compound 1 and derivatives at the indicated concentrations. The gray squares represent strains with deletions in essential genes and the black dots strains with deletions in nonessential genes. Shared sensitive strains are labeled. In each HIP profile, SET6, a previously published indicator for ergosterol inhibition, is the most sensitive and relevant (as measured by the Z score) hit identified. The second-most-relevant hit is ERG11, the lanosterol 14-alpha-demethylase, the target of azole antifungals. In the HOP profile, the Erg11p regulator DAP1 and a common set of deletion strains that have published genetic interactions with ERG11 or are hypersensitive to azoles scored reproducibly. (E) Compound 4, the inactive derivative of compounds 2 and 3, did not score any relevant sensitive (less than −5/−5) hits at 200 μM. (F) HIP HOP profiles of voriconazole, an established Erg11p inhibitor, show the same hits observed with compound 1 and its active derivatives. (G) Alignment of the HIP HOP Z score of compound 1 with that of voriconazole shows a high degree of correlation and conservation of hits.