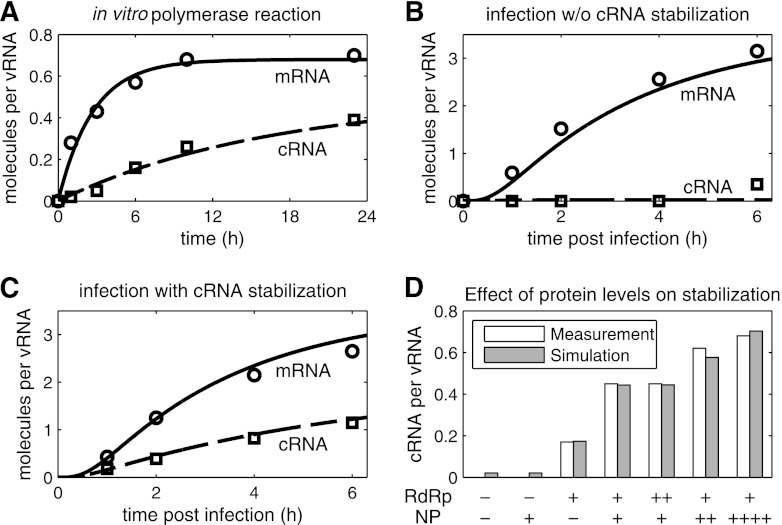
Fig 3.
Simulation of cRNA stabilization hypothesis. Experiments yielding NA gene-specific mRNA (○) and cRNA levels (□) were conducted by Vreede et al. using primer extension analysis (58, 61). We obtained relative RNA levels from these studies by densitometric analysis and normalized each data point to the constant vRNA signal. (A) Fit to data of an in vitro polymerase assay using virion-derived vRNPs (58). (B and C) Model fit to infection of 293T cells with influenza A/WSN/33 at an MOI of 5 (58). In brief, protein synthesis during infection was inhibited, and plasmids expressing NP, PA, and PB2 (B) or NP, PA, PB2, and PB1a (C) were transfected prior to infection. (D) Same as panel C, except that various amounts of plasmids expressing PA, PB2, PB1a (RdRp), NP, or empty vector (−) were transfected prior to infection. Bars represent the cRNA level at 2 hpi. PB1a, catalytically inactive mutant PB1-D445A/D446A which forms polymerase complexes that do not synthesize viral RNAs but stabilize cRNA.