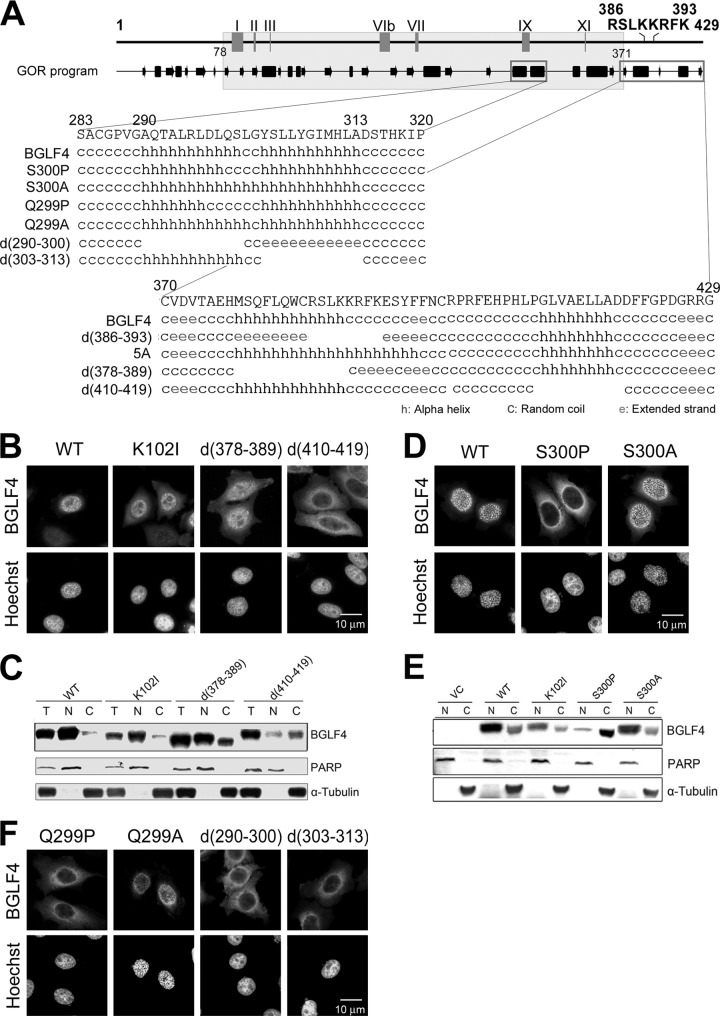
Fig 4.
The C-terminal helical regions of BGLF4 contribute to its nuclear localization. (A) Predicted secondary structures of the BGLF4 C-terminal region (i) aa 283 to 320 and (ii) 370 to 429 of BGLF4. (B) HeLa cells were transfected with plasmids expressing WT, K102I, d(378-389), or d(410-419). At 24 h posttransfection, cells were fixed and stained for BGLF4 and DNA. (C) Subcellular fractionation analysis of WT, K102I, d(378-389), or d(410-419) was performed, and results were analyzed by immunoblotting. (D) Slide-cultured HeLa cells were transfected with plasmids expressing WT, S300P, or S300A. An immunofluorescence assay was used to detect the distribution of BGLF4. (E) Subcellular fractionation of WT, S300P, or S300A was performed and analyzed by immunoblotting. (F) Immunofluorescence detection of the distribution of Q299P, Q299A, d(290-300), or d(303-313) of BGLF4 in transfected HeLa cells.