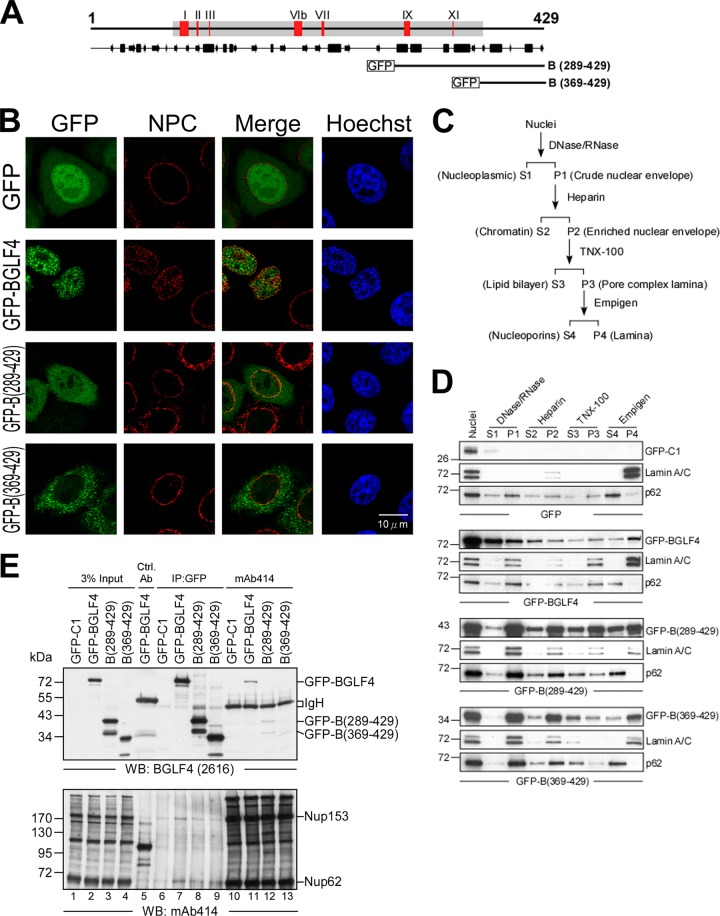
Fig 6.
The C terminus of BGLF4 associates with the nuclear envelope. (A) Schematic illustration of full-length and truncated GFP-BGLF4 constructs. (B) Slide-cultured HeLa cells were transfected with plasmid expressing GFP-BGLF4, GFP-B(289-429), or GFP-B(369-429) or vector control. At 24 h posttransfection, cells were fixed and stained for NPC with FG repeat-containing nucleoporin-specific mAb414 antibody, and DNA was stained with Hoechst 33258. The distribution of GFP-BGLF4 fusions and NPC was observed with a confocal microscope. (C) Scheme of fractionation of the various compartments of the nuclear envelope. The proteins associated with the nuclear envelope were finally fractionated into soluble nucleoporins (S4) or insoluble nuclear lamina (P4) fractions. (D) Nuclear envelope fractionation of HeLa cells expressing GFP, GFP-BGLF4, GFP-B(289-429), or GFP-B(369-429). Lamin A/C and nucleoporin p62 serve as the markers of nuclear lamina and nuclear pore complex, respectively. S, supernatant; P, pellet. (E) Cell lysates harvested from HeLa cells transfected with the GFP-BGLF4, GFP-B(289-429), or GFP-B(369-429) plasmid or GFP vector control were subjected to coimmunoprecipitation assay. Protein complexes were immunoprecipitated with rabbit anti-GFP antiserum or mAb414 antibody, and the immunocomplexes were detected in immunoblots using BGLF4-specific MAb 2616 or mAb414. The control antibody (Ctrl. Ab.) is a monoclonal antibody against GST. WB, Western blot.