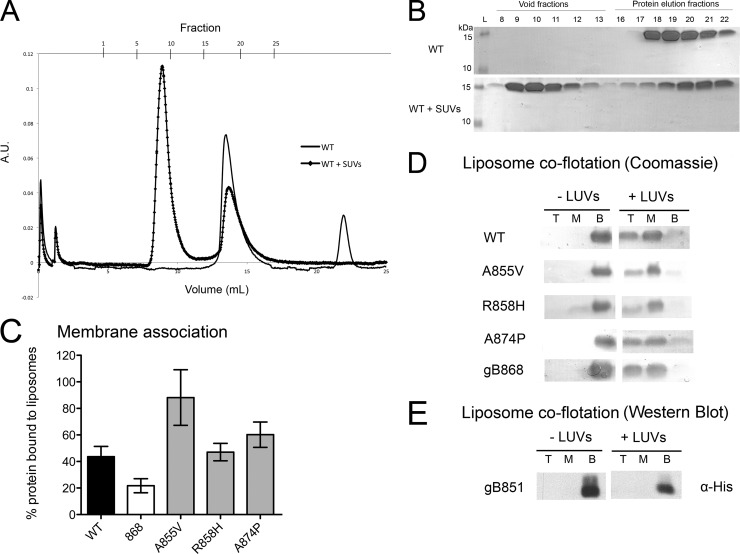
Fig 5.
Membrane binding by the WT and mutant gB cytodomains. (A to C) Association of soluble WT or mutant cytodomain proteins with anionic SUVs as assessed using liposome coelution in size exclusion chromatography. Soluble WT protein was passed over a Superose 12 column alone (solid line) or following incubation with anionic SUVs (squares). A.U., absorbance units. (B) Representative Coomassie-stained gels of fractions from the chromatogram shown in panel A. The presence of protein in the void fractions indicates binding of the protein to the SUVs. (C) Extent of binding was determined as bound/(bound + unbound) × 100%. (D and E) Stable association of soluble cytodomain proteins with (+) or without (−) anionic LUVs as assessed using liposome coflotation in a sucrose gradient. Total protein was precipitated with TCA out of the top (T), middle (M), and bottom (B) fractions of the gradient, analyzed by SDS-PAGE, and detected by Coomassie staining (D) or by Western blotting performed with anti-His antibody (E).