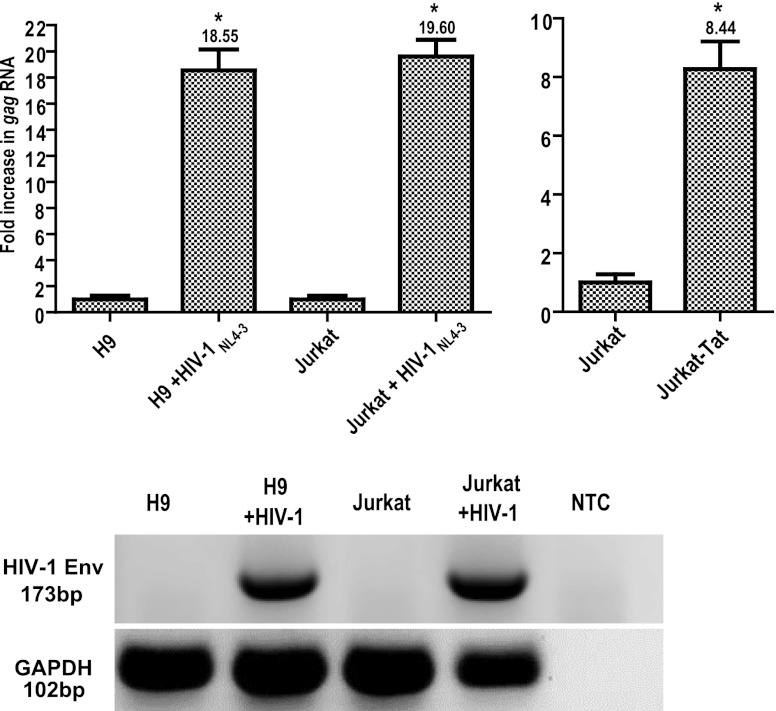
Fig 1.
HIV-1 infection and Tat stimulate HERV-K (HML-2) gene expression. Total cellular RNA was isolated from cells that were infected with HIV-1NL4-3 (for 1 week) or left uninfected. RNA was amplified using primers specific for HERV-K (HML-2) gag through one-step qRT-PCR and quantified using a standard curve generated by amplification of HERV-K (HML-2) gag RNA standards. The data are expressed as the fold increase over uninfected cells, with uninfected cells shown as normalized to 1 for simplicity of comparison. The rightmost panel shows Jurkat-Tat HERV-K (HML-2) gag RNA levels compared to levels in the parental Jurkat T cell line, with Jurkat T cell gag RNA levels normalized to 1. HIV-1 env and GAPDH one- step RT-PCR amplifications were also performed on the RNA to verify infection status and integrity of the material (NTC, nontemplate control). Error bars indicate the standard deviations (SD) for the results of three independent experiments. Significance was calculated by comparing infected samples with their uninfected counterparts using a Student t test and significant results are indicated (*, P < 0.005).