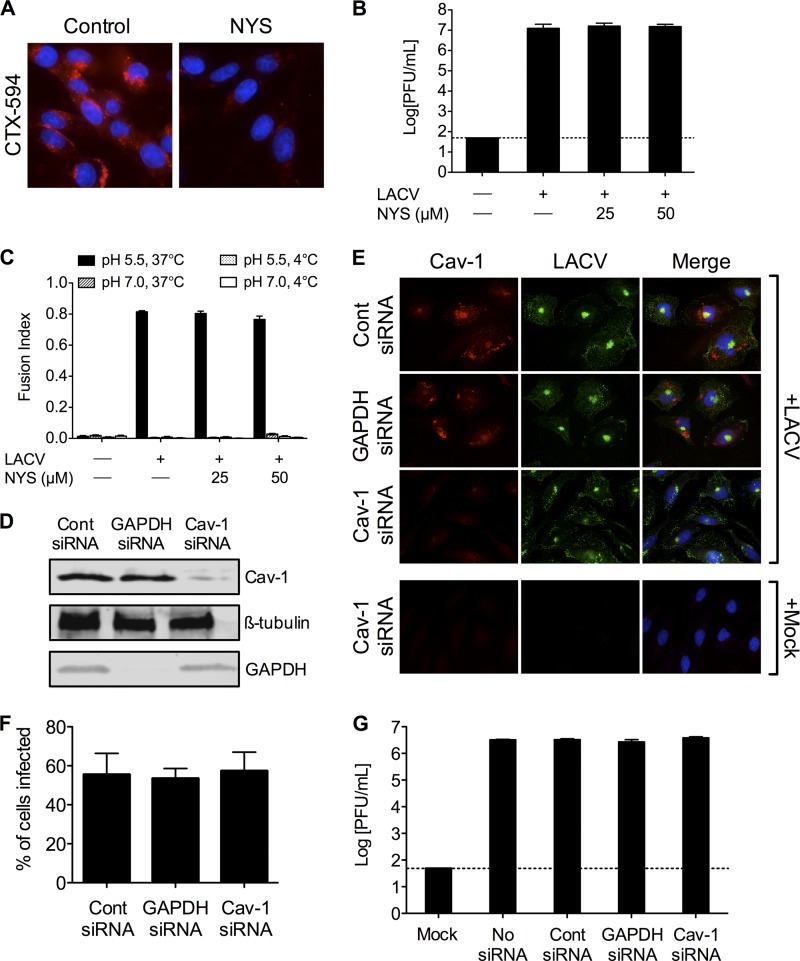
Fig 7.
LACV infection is not dependent on caveolar endocytosis. (A) Nystatin blocks uptake of cholera toxin subunit B. To confirm the activity of nystatin (NYS), BHK-21 cells (untreated or pretreated with NYS [25 or 50 μM]) were incubated with Alexa Fluor 594-conjugated cholera toxin subunit B (CTX-594). After 45 min, cells were fixed and analyzed by fluorescence microscopy for the uptake of CTX-594. Nuclei (blue) were stained with Hoecht's stain. Only the higher concentration of NYS is shown. (B) LACV replication is not affected by NYS treatment. BHK-21 cells were infected with LACV (MOI, 0.005) in the presence of NYS for 1 h. Supernatants were harvested 24 h postinfection. (C) LACV FFWI is unaffected by inhibiting caveolar endocytosis. BHK-21 cells were mock infected or infected with LACV (MOI, 0.5) in the presence of NYS for 1 h. The dashed line represents the limit of detection. (D) HeLa cells were serially transfected with siRNA (control [cont], GAPDH, or caveolin-1 [Cav-1]). Cell lysates were subjected to Western blotting for Cav-1, GAPDH, and ß-tubulin to confirm knockdown. (E) Knockdown of Cav-1 does not decrease LACV infection. Twenty-four h after LACV infection (MOI, 0.5), HeLa cells were fixed and stained with anti-LACV Gc (green) and anti-Cav-1 (red) antibodies, followed by anti-mouse IgG and anti-rabbit IgG conjugated to FITC and TRITC, respectively. (F) The number of LACV-infected cells was counted, and the percentage of cells infected with LACV was determined for each condition. (G) Knockdown of Cav-1 does not decrease LACV titers. HeLa cells were infected with LACV (MOI, 0.01) 24 h following the second siRNA transfection. Supernatants were harvested 24 h postinfection. Viral titers were determined by standard plaque assays.