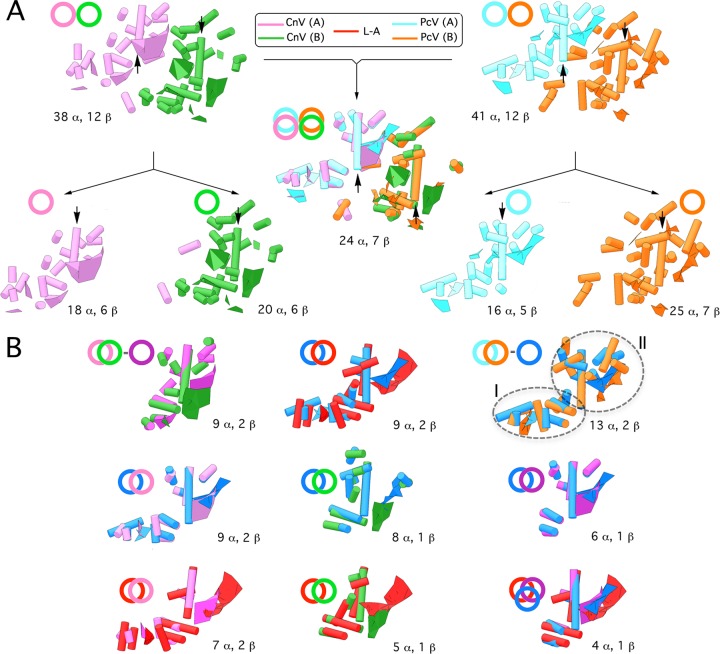
Fig 3.
Structural comparison of CnV, PcV, and L-A capsid proteins. (A) Superimposition (center) of CnV1 CP SSE (half-protein A, purple; half-protein B, green) (left) on PcV CP SSE (half-protein A, blue; half-protein B, orange) (right). Total numbers of SSE with close relative spatial locations are indicated (24 putative α-helices and 7 putative β-sheets). Black arrows indicate the ∼25 (purple)- and 35 (green)-Å rodlike densities of both CnV1 CP halves and the two ∼37-Å putative α-helices (blue and orange) of PcV CP elements. CnV1 and PcV CP are divided into their protein halves A and B (total number of SSE indicated, bottom). Circles and superimposed circles for each model (top) indicate structural superimpositions. (B) Superimposed views of conserved SSE in CnV1 protein halves A and B (conserved SSE, dark-purple circle) (top row, left). Superimposition of conserved SSE in PcV protein halves A and B (conserved SSE, dark-blue circle). The PcV conserved core is subdivided into domains I and II (top row, right). Superimposition of helical and planar regions of selected L-A Gag SSE (red) and conserved PcV SSE (dark blue) (top row, center). Superimposition of the PcV conserved core (dark blue) with CnV half-protein A (left), CnV1 half-protein B (center), or CnV1 conserved core (dark purple) (middle row). Superimposition of the L-A Gag conserved core (red), CnV1 half-protein A (left), and CnV1 half-protein B (center). Motif conserved in CnV1 and PcV halves with L-A Gag (right) (bottom row). These structural matchings preserve the spatial orientation of CnV1, PcV, and L-A capsid protein structural units within their capsids.