Fig 1.
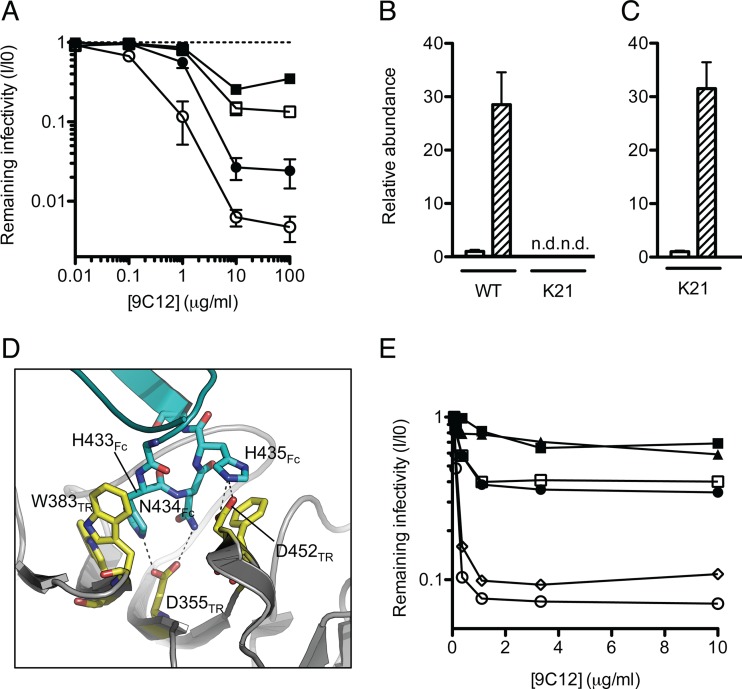
ADIN is essential for efficient neutralization of adenovirus. (A) Antihexon monoclonal antibody 9C12 was titrated against adenovirus on clonal fibroblast (MEF) lines derived from wild-type (WT) (n = 8) (circles) or TRIM21 knockout (K21) (n = 8) (squares) mice. Cells were either untreated (closed symbols) or treated with IFN-α (open symbols). Data represent mean remaining infectivities (I/I0) from the addition of antibody versus a PBS-treated control infection ± standard errors of the means. (B) TRIM21 mRNA levels were quantified by qPCR in unstimulated (white bars) or IFN-α-stimulated (hatched bars) MEF cells. n.d., not detected. (C) Levels of the transgene that disrupts the TRIM21 locus in K21 cells were measured by qPCR. Shading is as described above for panel B. (D) The previously solved structure of the TRIM21-IgG Fc complex (14) showing interactions between TRIM21 (yellow) (residues labeled TR) and the IgG Fc HNH motif (blue) (residues labeled Fc). (E) Antihexon monoclonal antibody 9C12 was mutated at three positions or expressed as the wild type. Antibodies were titrated against adenovirus on HeLa cells. Open circles, WT 9C12; closed circles, H433A mutant; open squares, N434A mutant; closed squares, N434D mutant; triangles, H435A mutant; diamonds, K219R mutant.