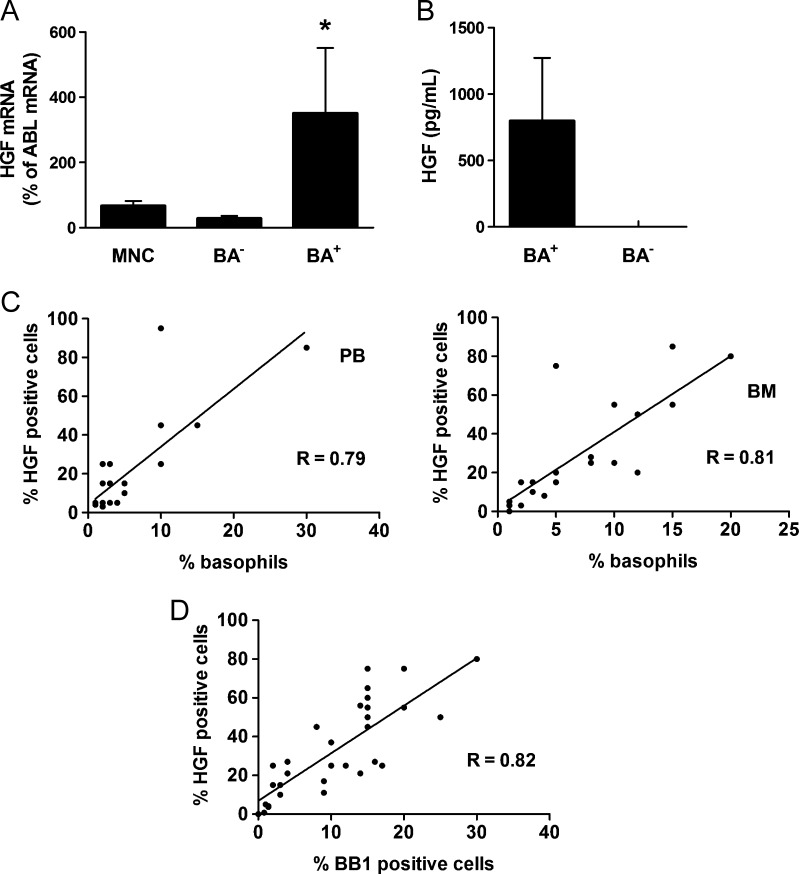
Figure 2.
Identification of basophils as a source of HGF in CML. (A) Expression of HGF mRNA in unfractionated PB MNCs, highly purified sorted CD203c+ basophils (BA+), and basophil-depleted (BA-) cells. MNC were prepared from PB of three CML donors. mRNA levels were quantified by qPCR using primers specific for HGF and ABL. Results show HGF mRNA levels as percent of ABL mRNA levels and represent the mean ± SD from three donors. *P < .05 compared with MNC. (B) Measurement of HGF protein levels in supernatants of cultured PB cells (5-day culture) obtained from three patients with CML with marked basophilia (>10%) and three patients with CML with low basophil counts (≤2%). HGF levels were determined by ELISA. Results represent the mean ± SD of three donors. (C) Correlations between HGF+ cells and basophils (Wright-Giemsa stain) in BM MNC samples (n = 20, left panel) and PB MNC (n = 17, right panel) of patients with CML. The numbers (percentage) of HGF+ cells were determined by IHC. R indicates the correlation coefficient. (D) Correlation between HGF+ cells and BB1+ cells (percentage of nucleated cells) in BM sections in patients with CML (n = 29). Adjacent BM sections were stained with antibodies against HGF and BB1 by IHC. R indicates the correlation coefficient.