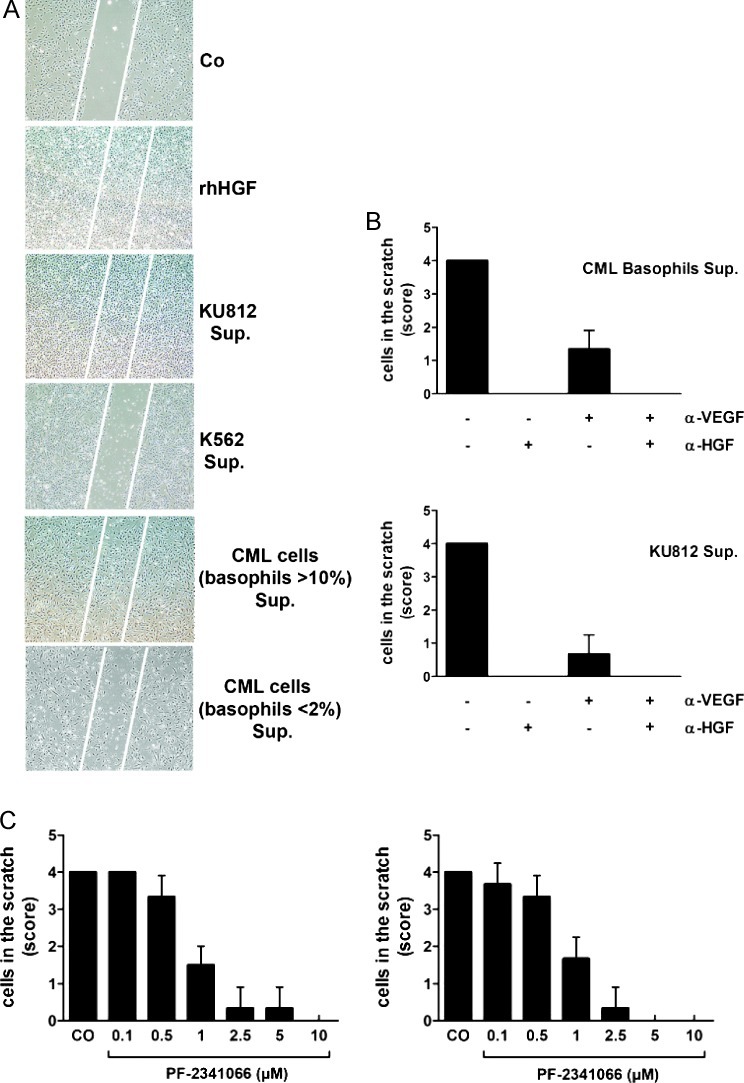
Figure 5.
Effects of basophil-derived HGF on endothelial cell migration. (A) Effects of rhHGF and CML-derived HGF on migration of HUVECs in a scratch wound assay. Confluent HUVEC layers were prepared in six-well plates. A linear scratch wound (≈ 100 µm diameter) was produced by a pipette tip. Then, HUVECs were cultured in control medium (CO), rhHGF (100 ng/ml), or 5-day supernatants (Sup.) of KU812 cells, K562 cells (HGF-negative), and primary CML cells (CML-enriched fractions, > 10% basophils; and CML fractions containing < 2% basophils= negative control). After 24 hours, migration of HUVEC was examined under an inverted microscope magnification: 4x/0.13. The scratch wound is marked by white bars. (B) Effects of a neutralizing anti-HGF antibody (αHGF) and a neutralizing anti-VEGF antibody (αVEGF) on migration of HUVECs determined by scratch wound migration assay. After introducing a scratch wound, HUVECs were incubated with supernatants (Sup.) of primary basophil-rich CML cells (>10% basophils) or KU812 cells in the absence (-) or presence (+) of αHGF (60 ng/ml) or/and αVEGF (100 ng/ml) as indicated. After 24 hours (37°C), migration of HUVECs was examined under an inverted microscope and photographed. Cell density in the scratch was scored from 0 to 4 as shown in Figure W1. Results represent the mean ± SD of three independent experiments. (C) Effects of the c-Met inhibitor PF-2341066 on migration of HUVECs induced by KU812 cell supernatant (left panel) or supernatant of primary basophil-rich cells (right panel). After a linear scratch was produced, HUVEC monolayers were incubated with supernatants of CML cells in the absence (CO) or presence of various concentrations of PF-2341066 as indicated. After 24 hours, migration of HUVECs was examined under an inverted microscope and photographed. Cell density in the scratch was scored from 0 to 4 as shown in Figure W1. Results represent the mean ± SD of three independent experiments.