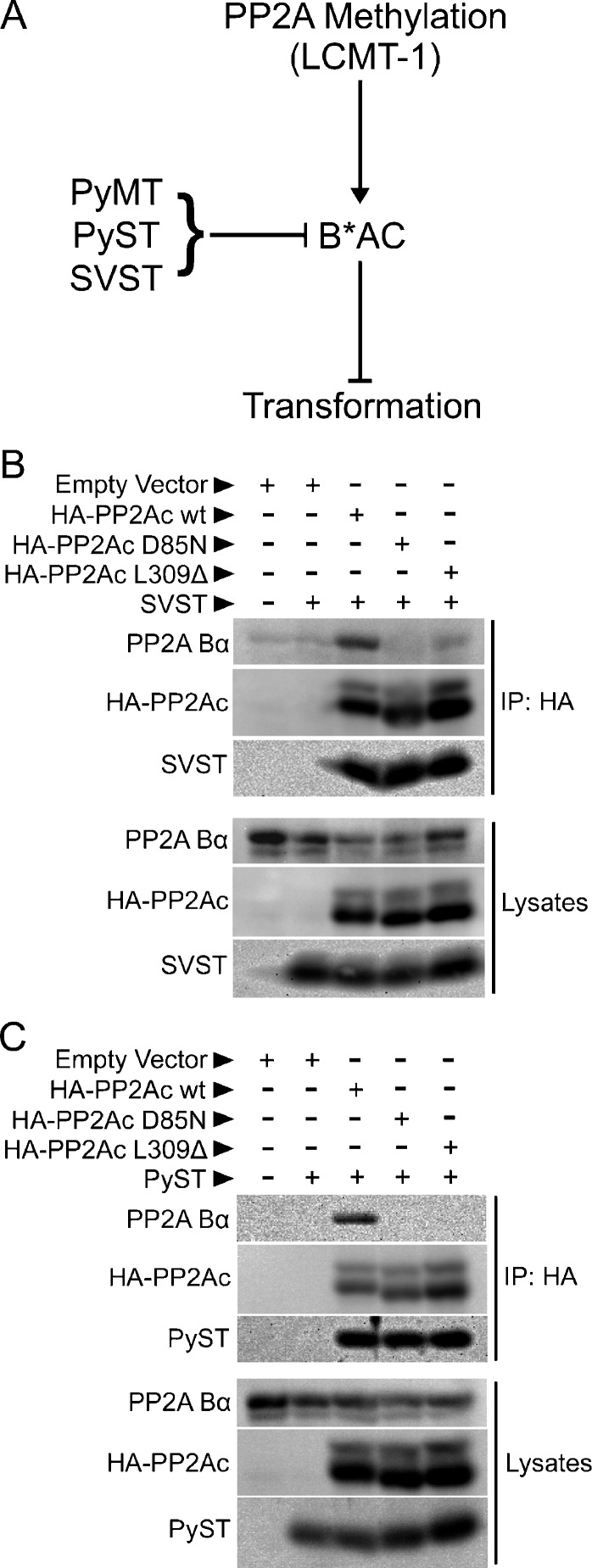
Figure 1.
Unlike the methylation-dependent cellular B-type subunit, Bα, SVST and PyST can incorporate into PP2A heterotrimers independently of PP2Ac carboxyl methylation. (A) The diagram illustrates a potential strategy of polyomavirus and SV40 in which methylation-insensitive viral B-type subunits (PyMT, PyST, and SVST) specifically replace methylation-sensitive cellular B-type subunits (B*), thus promoting transformation by circumventing normal control of PP2A by methylation. LCMT-1 promotes PP2Ac subunit methylation and the assembly of methylation-sensitive B-type subunits into PP2A heterotrimers (B*AC), which block transformation. Specific targeting of PP2A B*AC complexes by MT and ST oncoproteins promotes transformation. (B and C) HEK 293 cells were cotransfected with empty vector, HA-tagged wild-type PP2Ac (HA-PP2Ac wt), HA-tagged PP2Ac D85N mutant, HA-tagged PP2Ac carboxy-terminal leucine deletion mutant (HA-PP2Ac L309Δ), and SVST (B) or PyST (C) in the combinations indicated. HA-epitope tagged PP2Ac was immunoprecipitated 48 hours later with a sepharose bead-conjugated anti-HA antibody for 1.5 hours at 4°C with rocking to determine the binding of endogenous Bα and SVST (B) or PyST (C). After washing twice with PBS and lysis buffer, immune complexes (upper panels) and lysates (lower panels) were resolved on a 12% SDS-PAGE gel and probed with antibodies to the HA epitope tag, Bα subunit and SVST (B), or PyST (C).