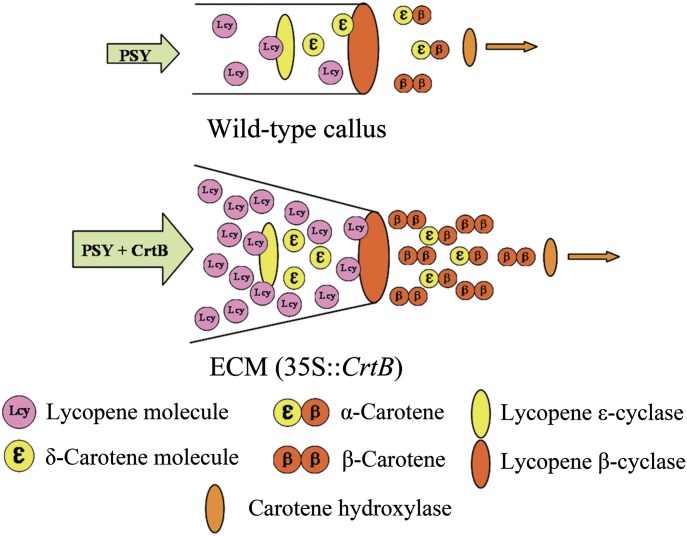
Fig. 10.
A hypothetical schematic model of carotenoid metabolic channels toward the β-carotene branch point in callus tissues. In wild-type callus, most of lycopene molecules can be captured by LCYE because of low carotenoid metabolism flux. In the ECMs, exogenous CrtB engineers a striking carotenoid metabolism flux. The activity of LCYE is unaltered. A mass of lycopene molecules diffuses to LCYB and is converted into β-carotene.