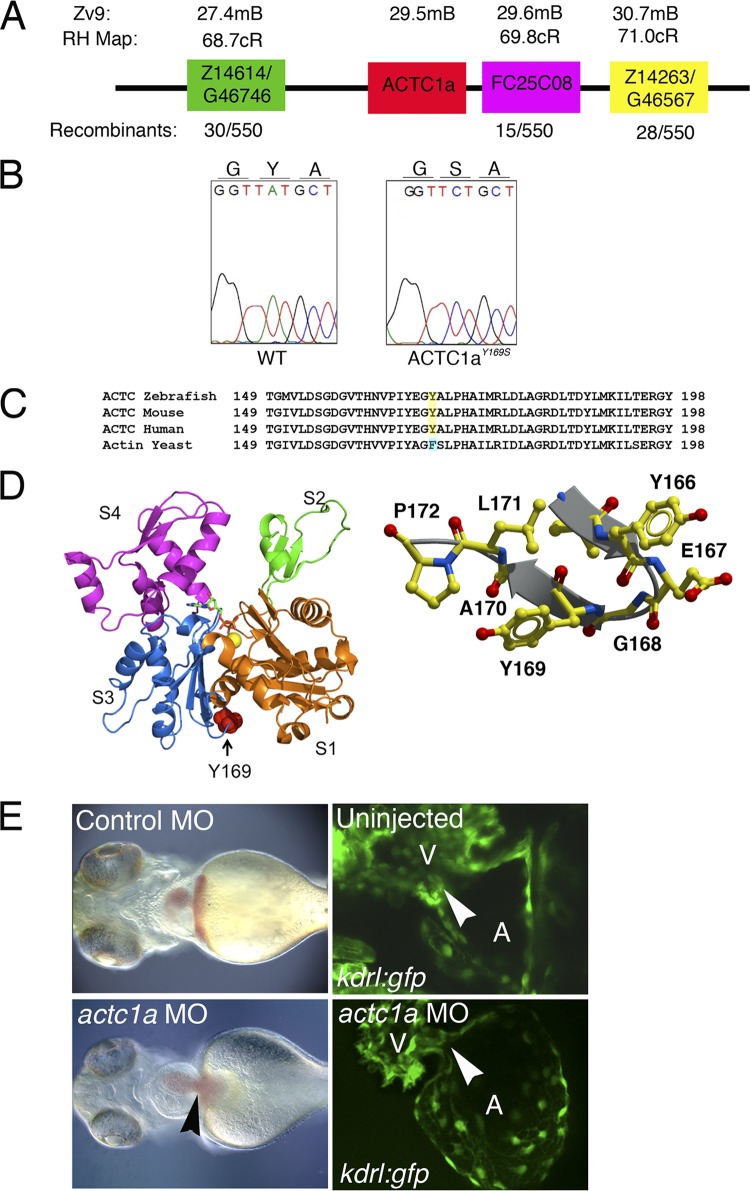
Fig 3.
s434 mutants display a point mutation in zebrafish alpha cardiac actin 1a gene (actc1a). (A) The actc1a gene is located on chromosome 20, at 29.5 Mb, between the zebrafish markers Z14614 and FC25C08, based on the Zv9 genome assembly. All markers correspond to the radiation hybrid (RH) map. Recombination is measured in centimorgans (cM). (B) Chromatogram showing that the s434 mutation is an A-to-C substitution at nucleotide 571 of actc1a, resulting in a tyrosine-to-serine amino acid change at amino acid 169 within the final proteolytically processed ACTC1a protein. (C) Protein alignment demonstrating that this tyrosine residue is evolutionarily conserved. Yeast cells have a phenylalanine at residue 169, an analogous aromatic residue. (D) Crystallization renderings of the actin monomer, highlighting the location of residue 169 in the W-loop (right side). Subunits S1 to S4 are marked. This part of the monomer is a nucleotide sensor, participating in ATP-ADP exchange. The image on the left shows the conformation of actin when ATP is bound. (E) Left panels, bright-field images indicate that the actc1a MO injection results in a heart-specific phenotype, with heart enlargement and edema (black arrowhead) observed at 48 hpf. (Right panel) Endocardial cushions do not form in the morphant, as observed in kdrl:GFP embryos (white arrowheads indicate the locations of the AVC). All images are oriented with the anterior portion to the left; the ventral view is shown.