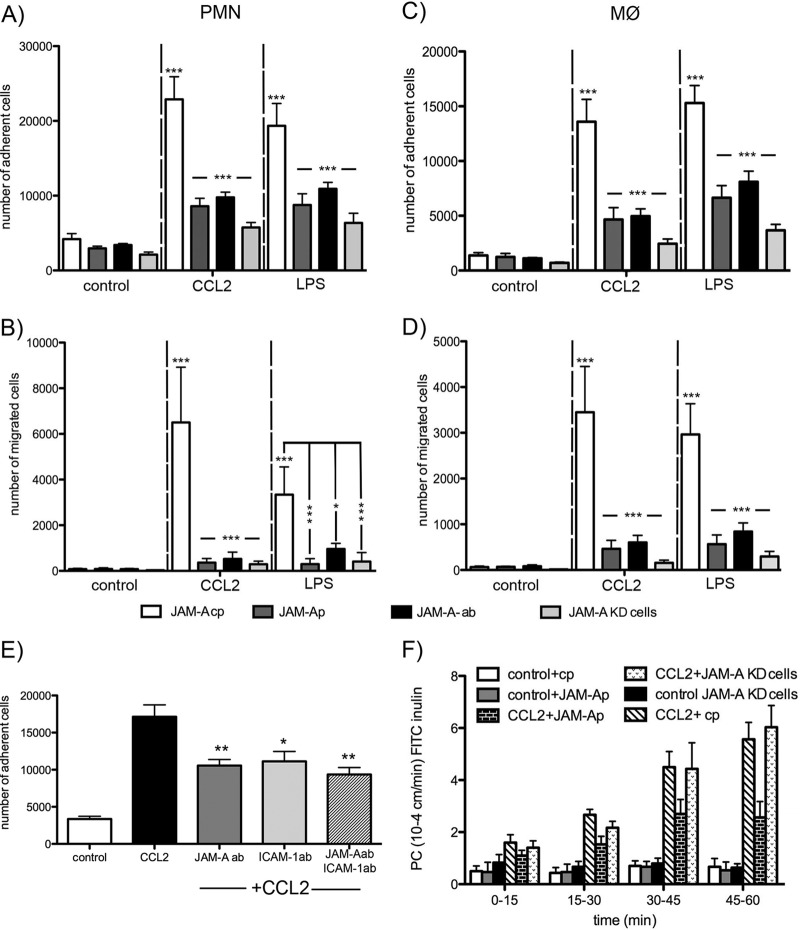
Fig 3.
Freshly prepared neutrophils (polymorphonuclear leukocytes [PMNs]) (A and B) and macrophages (MØ) (C and D) were labeled with calcein-AM and layered on top of mBMEC monolayers previously treated with CCL2, LPS, or vehicle in the presence of JAM-A-inhibitory peptide (JAM-Ap; 1 μg/ml), control JAM-A peptide (JAM-A-cp; 1 μg/ml), or neutralizing anti-JAM-A antibody (JAM-A-Ab; 10 μg/ml). As a control, we also used JAM-A-KD cells, generated by stable transfection of bEnd.3 cells with JAM-A shRNA. Cells were incubated for 2 h, and then the medium with nonadherent cells was removed and the sample was washed and fixed. The fluorescence was read on a fluorescent reader. Both CCL2 and LPS increased the number of adherent (A and C) and migrated (B and D) neutrophils and macrophages, and that was blocked by treatment with JAM-A-inhibitory peptide or JAM-A antibody or if JAM-A-KD cells were used. Data represent averages ± SDs for 3 independent experiments. *, P < 0.05; ***, P < 0.001. (E) Adhesion assay for neutrophils (polymorphonuclear leukocytes) under conditions of exposure of brain endothelial cell monolayer to CCL2. The adhesion was blocked by adding either neutralizing anti-JAM-A (10 μg/ml; R&D Systems), neutralizing anti-ICAM-1 (10 μg/ml; R&D Systems), or a cocktail of anti-JAM-A and anti-ICAM-A antibodies (both at a concentration of 10 μg/ml) (pretreated and treated for 1 h). Notice the significant reduction in polymorphonuclear leukocyte adhesion if JAM-A or ICAM-1 is blocked. However, there was no amplifying effect if two neutralizing antibodies were applied. Data represent averages ± SDs for 3 independent experiments. *, P < 0.05 compared with cells treated with CCL2 only; **, P < 0.01 compared with cells treated with CCL2 only. ab, antibody. (F) Recombinant murine CCL2 was applied at the top and bottom of a Transwell system. The permeability coefficient (PC) for FITC-inulin was evaluated from 0 to 60 min. CCL2 induced a time-dependent increase in permeability. Adding JAM-A-neutralizing peptide showed a partial protection of this opening of the brain endothelial cell barrier, but CCL2 still increased permeability in JAM-A-KD cells. Data represent averages ± SDs for 5 independent experiments.