Fig 6.
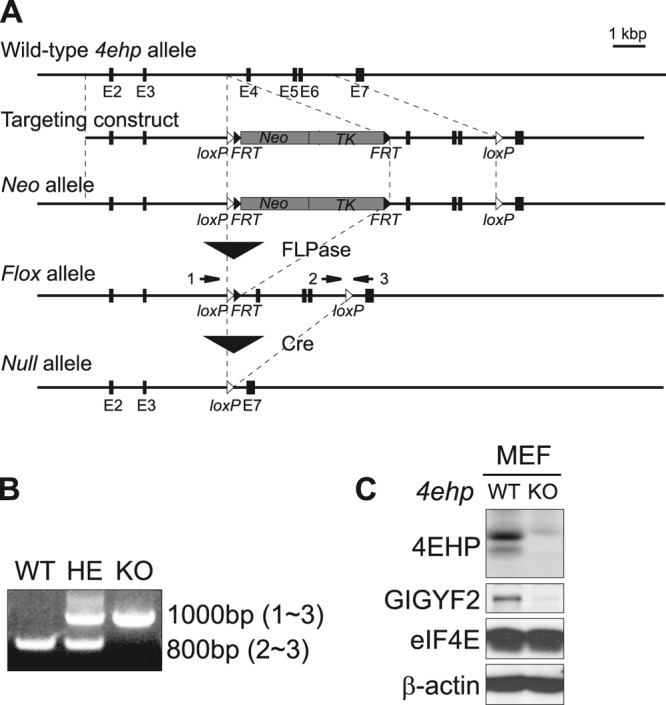
Disruption of the 4ehp gene in mice. (A) Schematic representation of the targeting construct used for the generation of 4ehp knockout mice. FRT and loxP sequences are indicated by black and white triangles, respectively. Negative (HSV-TK) and positive (PGK-neo) selection markers are indicated by gray boxes (TK, thymidine kinase; Neo, neomycin). Numbered black boxes represent exons in the 4ehp gene. The 4ehp neo allele was produced by homologous recombination. FLPase was used to generate the 4ehp flox allele. 4ehp null allele mice were produced by mating flox allele males with CMV-Cre females. (B) PCR genotyping of genomic DNA from mice with the 4ehp wild-type (WT), heterozygous (HE), and knockout (KO) genotypes. Arrows (numbered 1 to 3) in panel A denote annealing positions of oligonucleotides used for genotyping. (C) Immunoblotting of m4EHP, GIGYF2, and eIF4E proteins in 4ehp WT and KO MEFs. β-Actin was used as a loading control.
