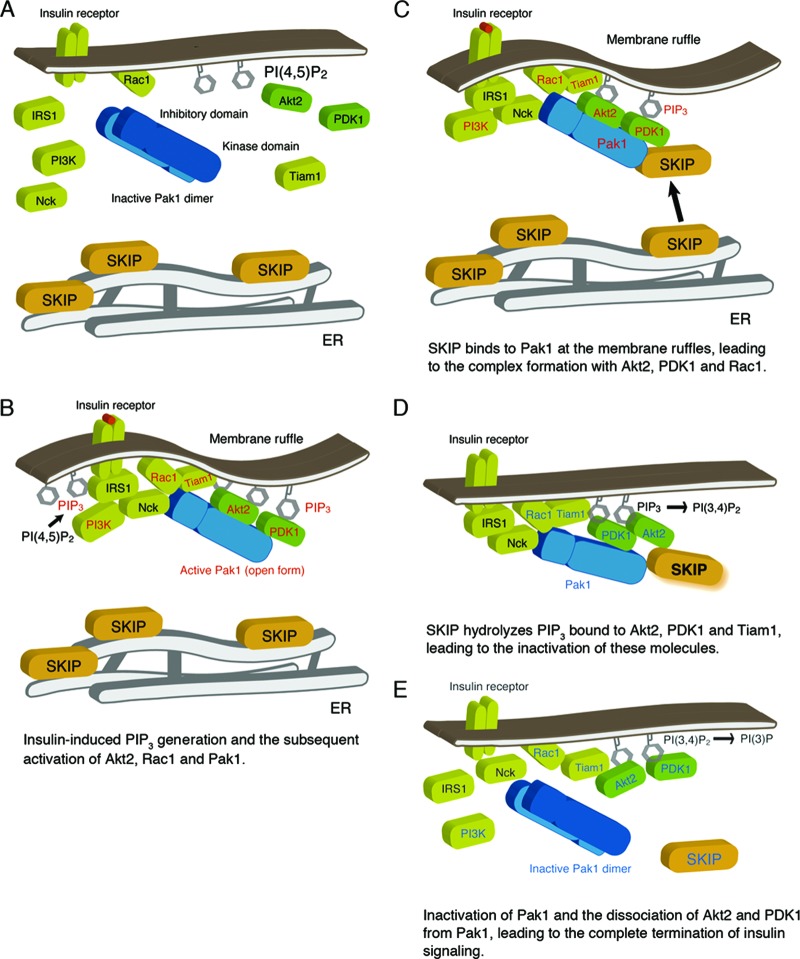
Fig 10.
Working model of SKIP regulation of insulin signaling. (A) Under resting conditions, SKIP is localized to the ER. (B) Insulin-dependent PIP3 generation and Rac1-dependent Pak1 activation. Pak1 activation triggers its recruitment to the insulin receptor complex and subsequent complex formation with Akt2 and PDK1. Activated signaling molecules are highlighted in red. (C) Insulin induces translocation of SKIP to the plasma membrane, where SKIP binds to active Pak1 (the open form). Formation of a complex including SKIP, Pak1, Akt2, and Rac1 is induced at the membrane ruffles. (D) SKIP hydrolyzes PIP3 bound to Akt2. Localization of SKIP in proximity to Akt2 facilitates its inactivation. Signaling molecules inactivated by SKIP are indicated in blue. (E) SKIP negatively regulates Rac1 and Pak1 activity, leading to the inactive conformation of Pak1. Dissociation of Akt2 and PDK1 from inactive Pak1 terminates insulin signaling.