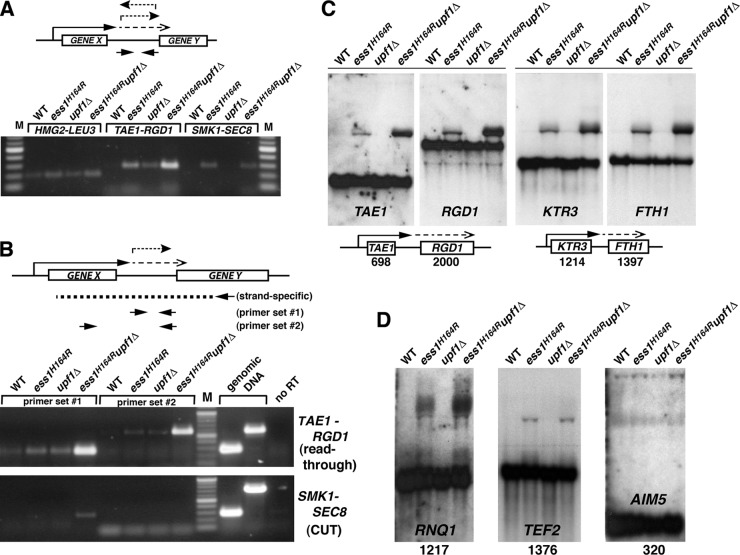
Fig 7.
Strong mRNA termination defects were detected in ess1 mutants using cells that lack nonsense-mediated decay. (A) Intergenic transcription is detected in ess1 mutants. Quantitative reverse transcription–RT-PCR was used to detect intergenic transcription. Results are shown for three representative loci, HMG2-LEU3, TAE1-RGD1, and SMK1-SEC8. Total RNA from the indicated strains was reverse transcribed using random hexamer primers, and the cDNA products were amplified by PCR for 30, 30, and 34 cycles, respectively, and visualized on an agarose gel. Intergenic primers were used for PCR as indicated in the schematic. (B) Ess1 mutants fail to terminate at mRNA genes, and the readthrough transcripts are degraded by NMD. In contrast to the experiment whose results are shown in panel A, gene-specific primers were used for first-strand cDNA synthesis (see schematic) to allow strand-specific detection of intergenic transcripts (primer set 1), as well as the longer fusion transcripts (primer set 2). The presence of long products at the TAE1-RGD1 locus in ess1H164R mutant cells indicates mRNA readthrough. Thirty cycles were used for PCR. Genomic DNA controls show the efficacy of the primers. Mixtures for control reactions without reverse transcription (no RT) contained 4× as much input template as the experimental samples. (C) Northern analysis of ess1 and ess1 upf1 double mutants and controls showing aberrantly long (readthrough) transcripts. Fifteen micrograms of total RNA was used. The 32P-labeled probes (specific activity, >5 × 108/μg DNA) were generated from the open reading frames of the genes indicated. The numbers refer to the sizes of the open reading frames in base pairs. Both the upstream and downstream gene probes at each locus were used. (D) Additional loci are analyzed as described for panel C, except that only the upstream gene probe for each locus was used. Ten micrograms of total RNA was used for these samples.