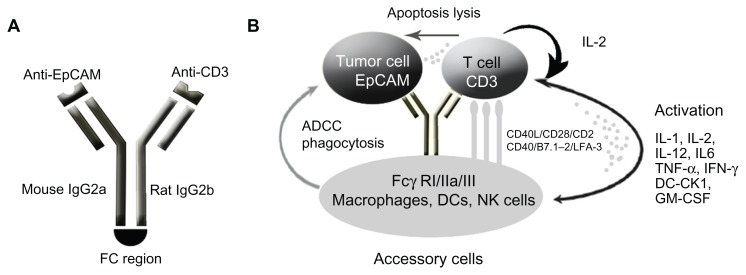
Figure 3.
Schematic of mode of action of catumaxomab. (A) Catumaxomab is a trifunctional monoclonal antibody with two different antigen-binding sites and a functional Fc domain. (B) The two specific antigen-binding sites bind to epithelial tumor cells via the epithelial cell-adhesion molecule (EpCAM) and to T cells via CD3, while activating Fcγ receptor I-positive, IIa-positive, and III-positive accessory cells (dendritic cells, macrophages and natural killer cells) via its functional Fc domain.