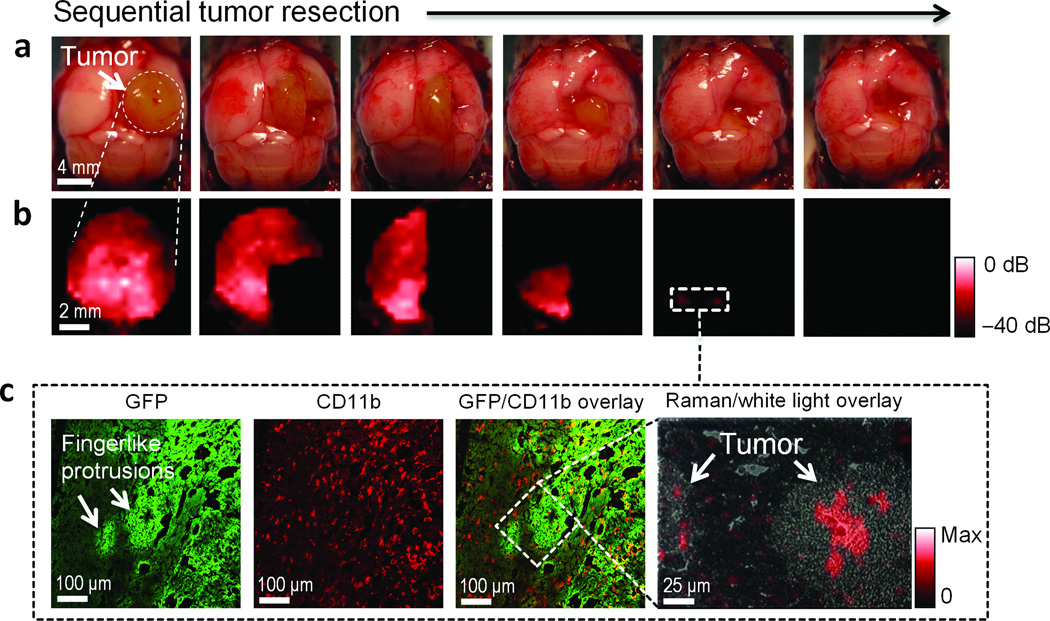
Figure 5. Raman-guided intra-operative surgery using MPRs.
a. Living tumor-bearing mice (n = 3) underwent craniotomy under general anesthesia. Quarters of the tumor were then sequentially removed (as illustrated in the photographs) and b. intra-operative Raman imaging was performed after each resection step, until the entire tumor had been removed by visual inspection. After the gross removal of the tumor, several small foci of Raman signal were found in the resection bed (outlined by dashed white square; some Raman images smaller than black square). Raman color scale in red from −40 to 0 dB. c. Subsequent histological analysis of sections from these foci demonstrated an infiltrative pattern of the tumor in this location, forming finger-like protrusions extending into the surrounding brain tissue. As shown in the Raman microscopy image (right), Raman signal was observed within these protrusions, indicating the selective presence of MPRs in these protrusions. Box not drawn to scale. Raman signal in linear red color scale.