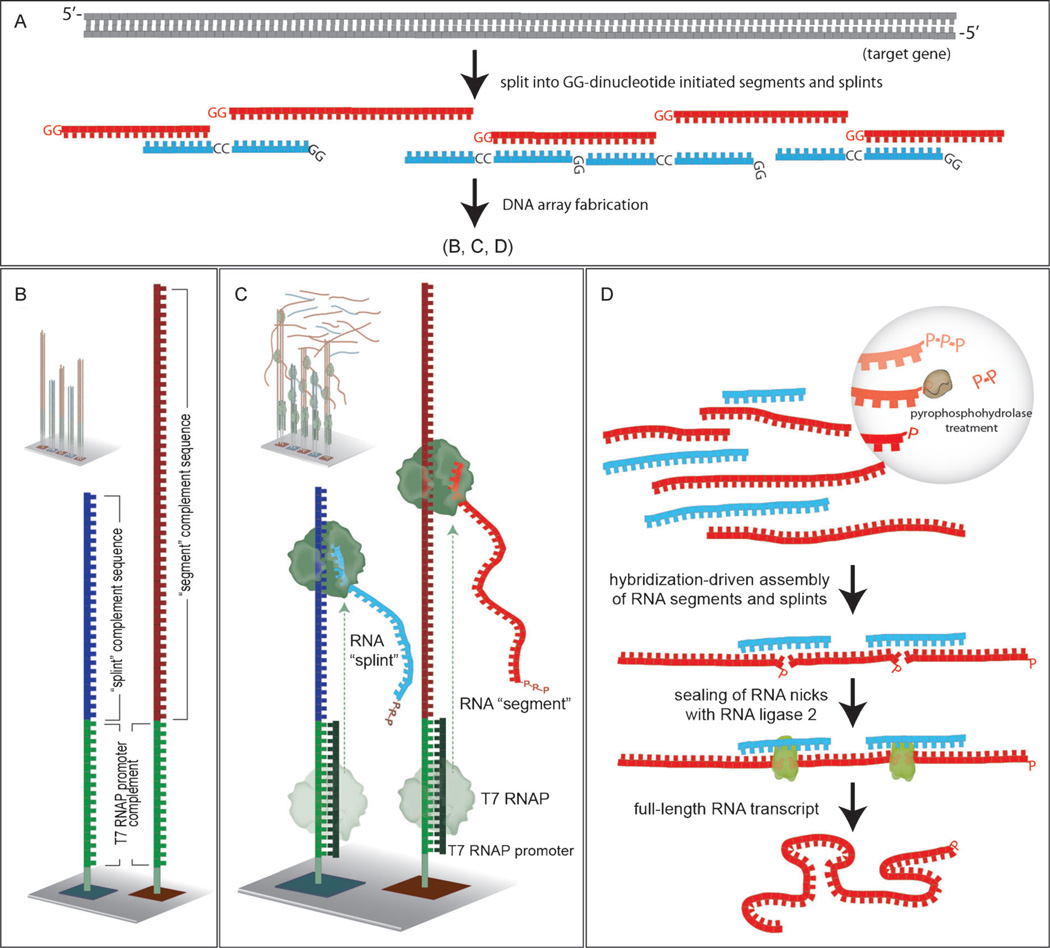
Figure 1.
Illustration of the RNA-mediated gene assembly process. A) Design of segment (red) and splint (blue) sequences to be employed. B) Segment (dark red) and splint (dark blue) complement sequences as synthesized on the DNA array with the complement of the T7 RNAP promoter sequence (green) at their 3′-termini. C) Hybridization of an oligonucleotide encoding the T7 RNAP promoter sequence yields the necessary double-stranded promoter, and addition of RNA polymerase causes transcription to occur. D) RNA segments and splints have their terminal triphosphate units trimmed to monophosphates, assembly occurs by RNA:RNA hybridization, and nicks are sealed to yield the desired full-length RNA.