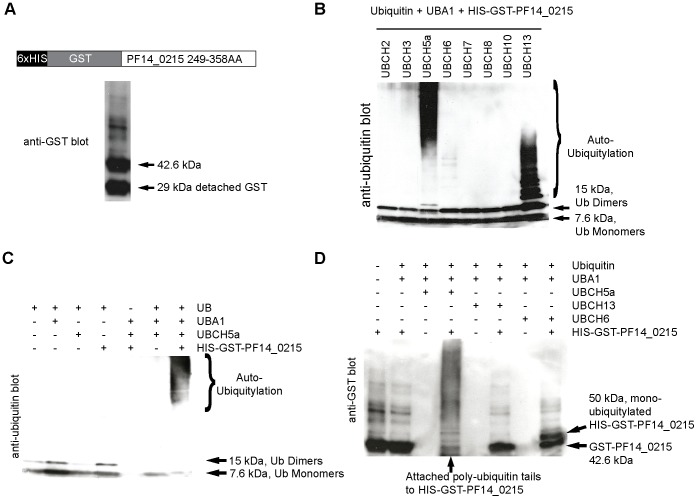
Figure 3. In vitro ubiquitylation assay of PfHRD1 (PF14_0215).
(A) Epitope-tagged recombinant PfHRD1 was expressed in E. coli and purified. Anti-GST immunoblot on purified protein extracts reveals the presence of detached free GST tags (MW = 29 kDa) and of PfHRD1-GST (MW = 42.6 kDa). (B) In vitro ubiquitylation assays were performed with commercial ubiquitin (Ub), human E1 UBA1, varying human E2 UBC enzymes (i.e., UBCH2, UBCH3, UBCH5a, UBCH6, UBCH7, UBCH8, UBCH10, and UBCH13), and our purified extract of epitope-tagged recombinant PfHRD1. Ubiquitylation patterns were revealed on anti-ubiquitin immunoblots. Different patterns of auto-ubiquitylation are observed with UBCH5a, UBCH13, and UBCH6. (C) In vitro ubiquitylation assays were performed in the presence (+) or absence (-) of commercial ubiquitin (UB), human E1 UBA1, human E2 UBCH5a, and our purified extract of epitope-tagged recombinant PfHRD. Ubiquitylation patterns were revealed on anti-ubiquitin immunoblots. Ubiquitylation is specifically observed only when all components are mixed together, including PfHRD1. (D) In vitro ubiquitylation assays were performed with commercial ubiquitin (Ub), human E1 UBA1, the human E2 enzymes UBCH5a, UBCH6, and UBCH13, and our purified extract of epitope-tagged recombinant PfHRD1. The attachment of ubiquitin on the recombinant PfHRD1 itself was detected by anti-GST immuno-detection. PfHRD1 is poly-ubiquitylated in the presence of UBCH5a and mono-ubiquitylated in the presence of UBCH6 whereas UBCH13 does not permit PfHRD1 auto-ubiquitylation.