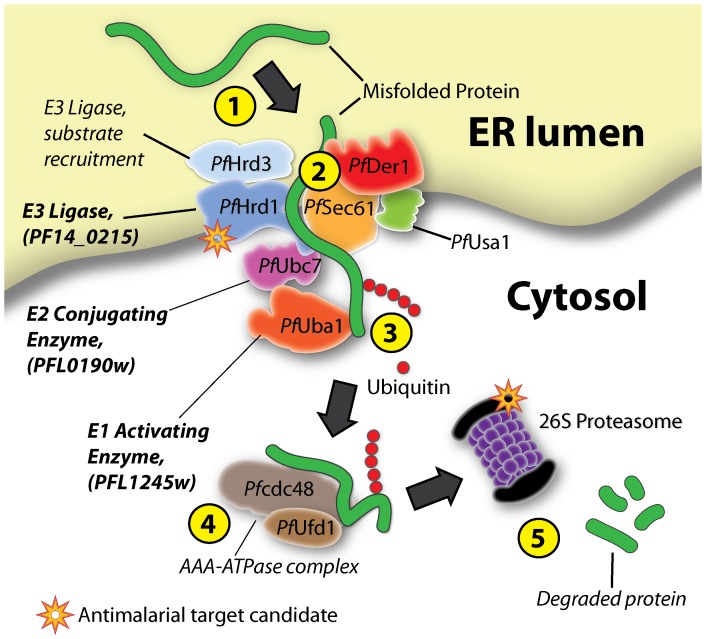
Figure 7. Graphical depiction of the Plasmodium ERAD pathway in protein quality control and its potential for antimalarial strategies.
Similar to their human and yeast counterparts, the components of the Plasmodium ERAD system likely serve to recognize and translocate misfolded ER luminal proteins to the cytosol for degradation by the 26S proteasome. A simplified flowchart is presented: (1) misfolded proteins are recognized and recruited to the ERAD complex, (2) where they are inserted across the ER membrane through a pore formed by a complex of ERAD proteins. (3) During translocation, the aberrant proteins are poly-ubiquitylated by the concerted action of the E1 ubiquitin-activating enzyme PfUBA1 (PFL1245w), the E2 ubiquitin-conjugating enzyme PfUBC (PFL0190w), and the E3 ligase PfHRD1 (PF14_0215). (4) The ubiquitylated aberrant proteins are extracted by the CDC48-UFD1-NPL4 AAA-ATPase complex and shuttled to the 26S proteasome (5) for degradation. Plasmodium ERAD drug target candidates are highlighted with an orange star.