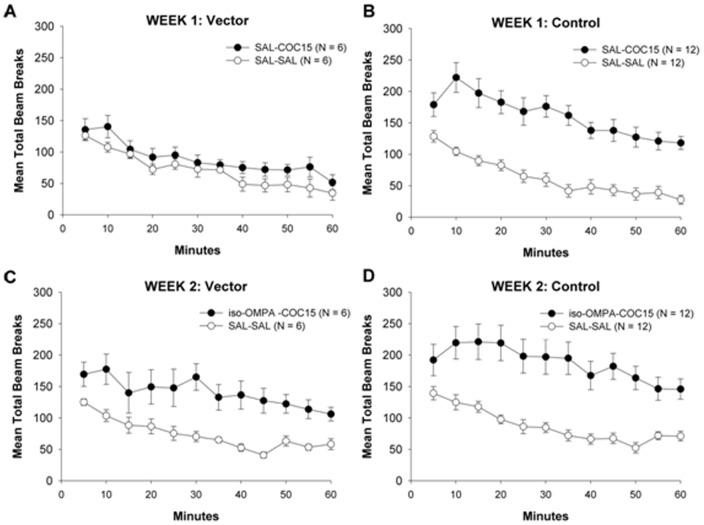
Figure 4. CocH suppresses rat cocaine locomotor response but enzyme inhibitor relieves suppression.
Rat locomotor activity is shown in “beam breaks" (mean ± SEM) per 5 min bin over a 60-min period of observation following an i.p. test injection of cocaine (15 mg/kg) or saline. On week 1 (A & B) rats were pretreated with i.p. saline, 2 hr before cocaine injection. On week 2 (C & D) they were pretreated at the corresponding time with i.p. iso-OMPA (1.5 mg/kg). “Vector" rats (N = 6) received 1011 particles of helper-dependent adenovirus via the tail vein approximately 1 month before testing, and a satisfactory level of cocaine hydrolase activity (>150 mU/ml) was confirmed in plasma samples drawn immediately after the final experiment. Control rats (N = 12) were pretreated only with saline. ANOVA confirmed a significant effect of cocaine injection in all groups except vector-treated rats in the absence of iso-OMPA.