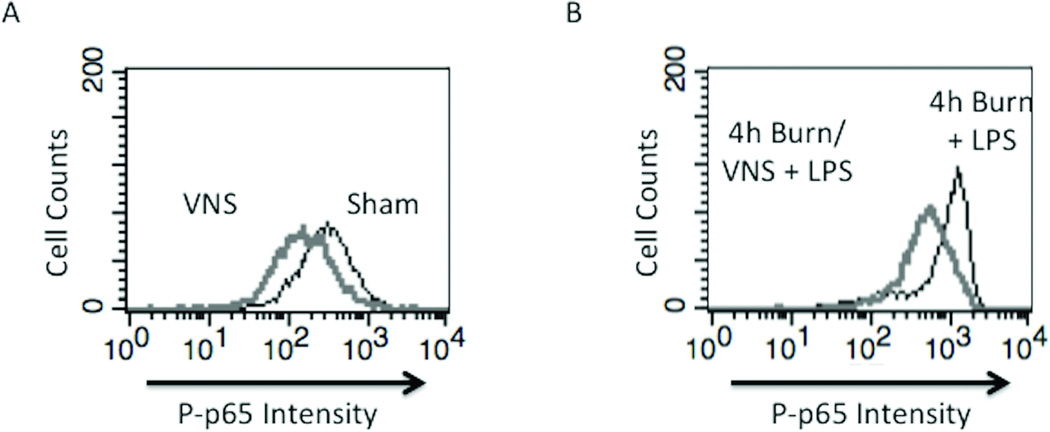
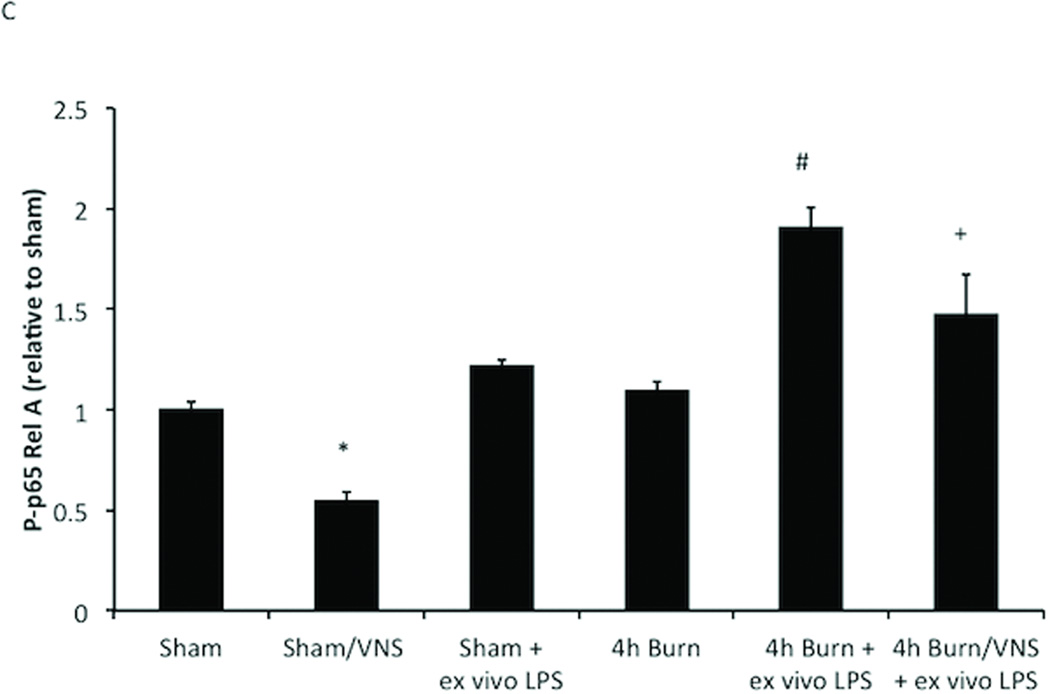
Figure 4. VNS decreases NF-KB activation in sham animals and negates macrophage hyper-responsiveness following burn injury.
(A) VNS treatment of sham animals reduced Phospho-p65 Rel A below baseline of unstimulated sham animals, demonstrating that VNS alters the inflammatory set-point in peritoneal macrophages. (B) Performing VNS prior to severe burn injury reduced the inflammatory response of peritoneal macrophages as measured by LPS induced Phospho-p65 Rel A levels using flow cytometry. (C) Graph representing flow based findings. Error bars represent SEM. * p < 0.005 vs. sham or 4 hour burn mice without VNS; # p < 0.001 vs. sham, VNS only or 4h burn; +p<0.005 vs. 4h burn + ex vivo LPS.