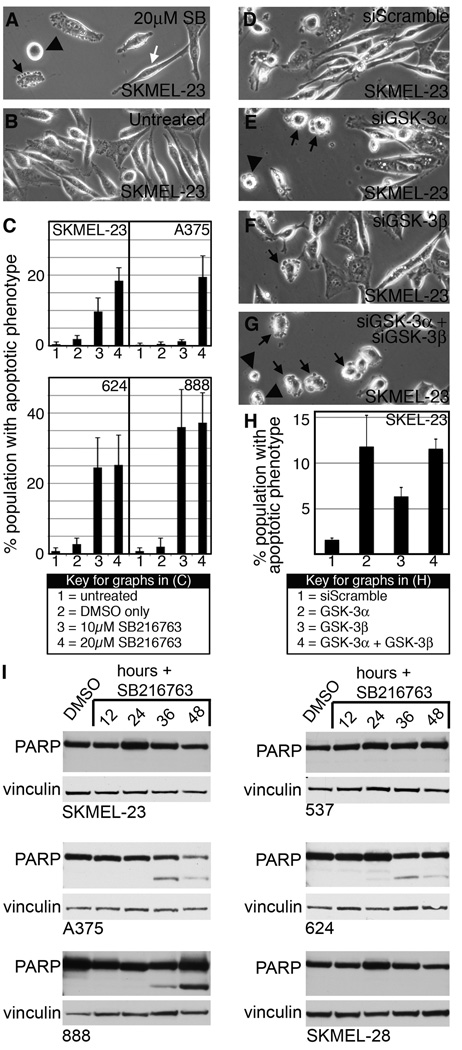
Figure 3.
GSK-3 inhibition induces apoptosis in melanoma cells. A–B, overall morphology of SKMEL-23 cells with (A) or without (B) SB216763 treatment at 9 hours. Cells displayed apoptotic phenotypes including blebbing (black arrow), rounding and adhesion loss (black arrowhead), as well as cells that maintain the parental phenotype (white arrow). C, quantification of apoptotic characteristics in melanoma cell lines upon GSK-3 inhibition. In six random fields, total cells and apoptotic cells were counted and graphed as a percentage of total population. Values are mean +/− s.d. (n=600 cells). D–G, SKMEL-23 cells transfected with siScramble (D), siGSK-3α (E), siGSK-3β (F), and both isoforms (G) were examined for apoptotic phenotypes 18 hours post-transfection. H, quantification of apoptotic phenotypes in D–G. Values are means +/− s.d. (n=900 cells) I, Western blots of melanoma cell lines treated with SB216763 for 12–48 hours compared to DMSO controls. Blots were probed with PARP antibody or vinculin antibody as a loading control.