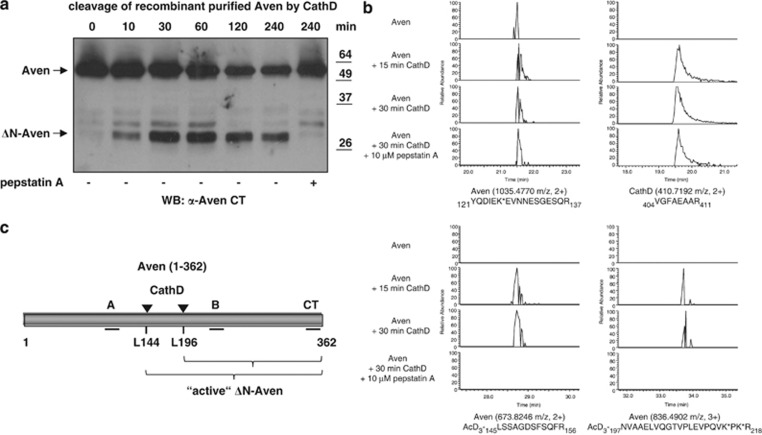
Figure 3.
Identification of CathD cleavage sites in the Aven protein by mass spectrometry. (a) Full-length Aven purified from HEK 293T cells was incubated with recombinant human CathD at pH 6.5. Time-dependent direct cleavage of Aven by CathD was evaluated by western blot analysis using the anti-Aven CT antiserum. Incubation for two hours without recombinant CathD failed to result in cleavage of the full-length Aven protein (data not shown). (b) Purified Aven protein was incubated with recombinant CathD, and newly formed alpha-N-terminal amines (and epsilon amines of lysine side-chains) were modified using trideutero-acetylation. Following trypsin digestion, LC-MS/MS analysis and peptide identification, peptides with trideutero-acetylated alpha-N-termini were considered as proteolysis-reporter peptides indicative of CathD processing. Extracted ion chromatograms (XIC) are shown for selected Aven and CathD peptides. Internal tryptic peptides with primary alpha-N-termini demonstrated the presence of both proteins in each sample (two upper panels). Two peptides with trideutero-acetylated N-termini reported protease cleavage at two positions in the Aven sequence when CathD was present without pepstatin A (two lower panels). Trideutero-acetylated lysine side-chains are indicated with an asterisk (*), and maximum Mascot score/threshold values were 139/38 (YQDIEK*EVNNESGESQR), 66/40 (VGFAEAAR), 62/39 (AcD3-LSSAGDSFSQFR) and 80/34 (AcD3-NVAAELVQGTVPLEVPQVK*PK*R). (c) A schematic diagram of the N-terminally Flag-tagged human Aven protein (aa 1–362). The binding sites for antisera used in this study (Aven CT, Aven A and Aven B) are indicated by black lines. The CathD cleavage sites (L144 and L196) that were identified by mass spectrometry analysis are labeled with arrowheads. Active ΔN-Aven represents the C-terminal fragment(s) produced by CathD cleavage, which displays anti-apoptotic activity