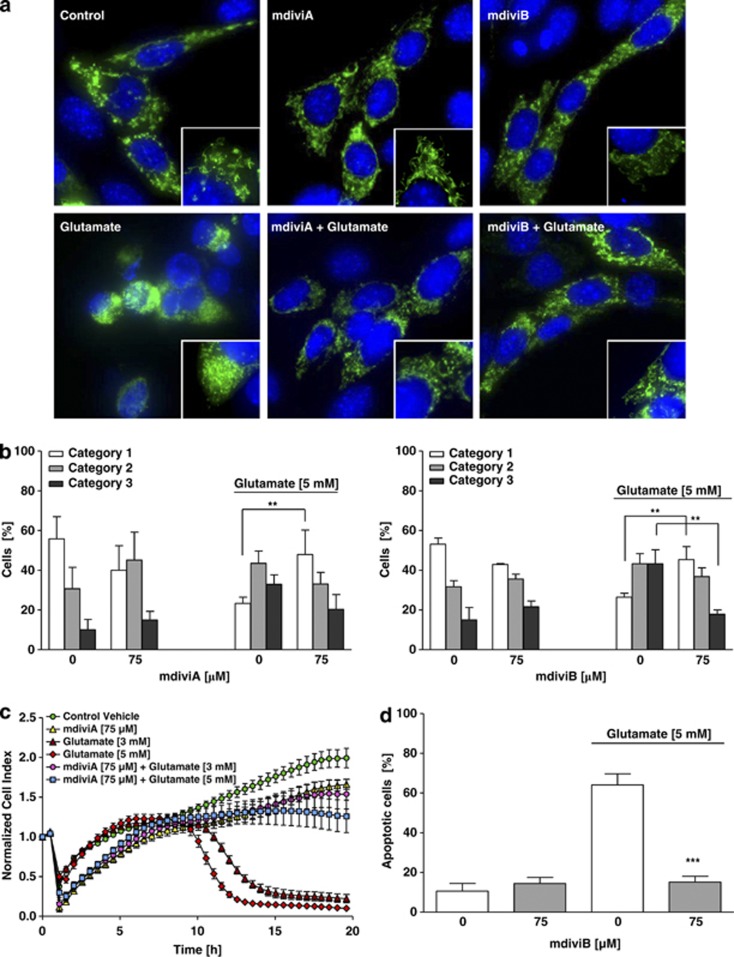
Figure 2.
The novel pharmacological inhibitor of Drp1, mdiviA, protects HT-22 cells against glutamate toxicity. (a) Fluorescence photomicrographs ( × 63 objective) of mGFP-transfected and DAPI-stained HT-22 cells show that Drp1 inhibitor mdiviA (75 μM) prevents fission of mitochondria in glutamate-exposed (5 mM, 18 h) HT-22 cells. (b) Quantification of mitochondrial morphology of ∼500 cells per condition: category 1 (elongated tubulin-like structure), category 2 (intermediate length) and category 3 (fragmented mitochondria). **P<0.01 category 1+2 mdiviA, mdiviB+glutamate compared with glutamate 5 mM-treated cells (n=3 independent experiments, ANOVA, Bonferroni-test). (c) HT-22 cells were cultured for 48 h in 96-well E-plates with 4500 cells/well and treated 24 h after seeding with 3 and 5 mM glutamate and mdiviA (75 μM) for 18 h (n=8). Representative graph of real-time detection of cellular impedance by xCELLigence System (Roche) is shown. (d) FACS analysis of HT-22 cells with n=10 000 cells per treatment condition after FITC-Annexin-V labeling to detect apoptotic cells. Exposure to glutamate (5 mM, 14 h) results in enhanced Annexin-V binding of apoptotic HT-22 cells compared with DMSO control. MdiviB (75 μM) significantly reduce glutamate-induced apoptosis. For statistical analysis, the experiments were repeated at least three times with an n=3 per treatment condition. ***P<0.001 compared with glutamate-treated cells (n=3, ANOVA, Scheffé's-test)