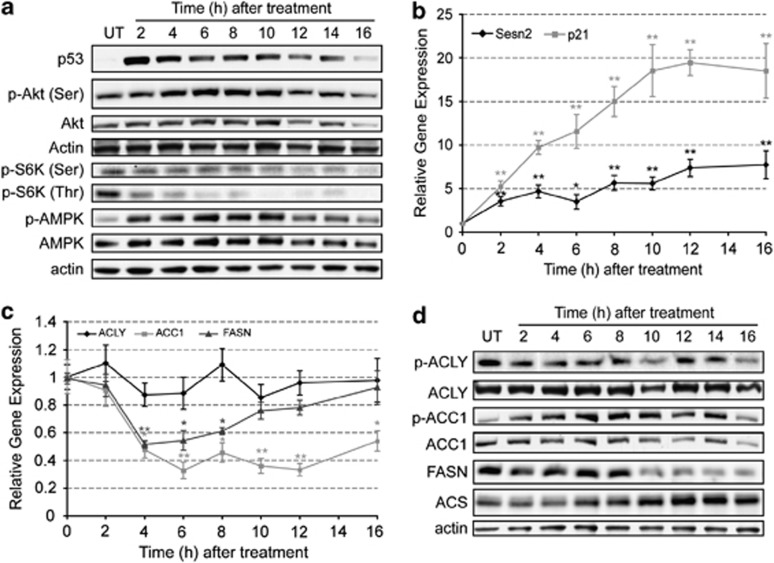
Figure 4.
Apoptosis modulates signaling pathways that alter gene expression, protein levels and phosphorylation status of lipogenic enzymes. EL4 cells were treated with 15 μM etoposide for up to 16 h and protein samples were obtained every 2 h. (a) Representative western blots showing of the effect of apoptosis induction on the levels of p53, Akt, p-Akt (Ser473), pS6K (Ser371), pS6K (Thr389), AMPK and p-AMPK (Thr172). Actin was used as an internal control for protein loading. (b) Expression levels of Sestrin 2 ( ) and p21 (
) and p21 ( ) obtained by quantitative polymerase chain reaction (PCR). Results are expressed in relation to their initial levels (untreated controls). Actin expression levels were used to normalize the results (mean±S.E.M.; *P<0.01, **P<0.001, n=3). (c) Expression levels of ACLY (
) obtained by quantitative polymerase chain reaction (PCR). Results are expressed in relation to their initial levels (untreated controls). Actin expression levels were used to normalize the results (mean±S.E.M.; *P<0.01, **P<0.001, n=3). (c) Expression levels of ACLY ( ), ACC1 (
), ACC1 ( ) and FASN (
) and FASN ( ) obtained by quantitative PCR. Results were normalized to the actin levels in each sample and expressed relative to the untreated control (mean±S.E.M.; *P<0.01, **P<0.001, n=3). (d) Western blot analysis of the levels of ACLY, p-ACLY (Ser454), ACC1, p-ACC1 (Ser79), FASN and ACS. Actin was used as an internal protein loading control. A representative sample is shown for each protein
) obtained by quantitative PCR. Results were normalized to the actin levels in each sample and expressed relative to the untreated control (mean±S.E.M.; *P<0.01, **P<0.001, n=3). (d) Western blot analysis of the levels of ACLY, p-ACLY (Ser454), ACC1, p-ACC1 (Ser79), FASN and ACS. Actin was used as an internal protein loading control. A representative sample is shown for each protein