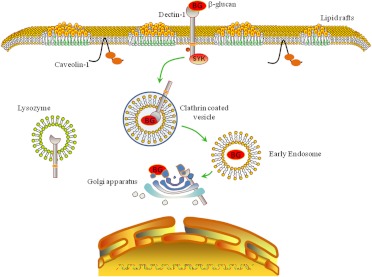
Fig. 7.
Schematic showing the proposed mechanisms for internalization and trafficking of soluble glucans by murine macrophages. In this model, soluble glucan is bound by membrane-associated Dectin-1, and the Dectin-1/glucan complex is rapidly internalized via a clathrin-dependent mechanism. The Dectin-1/glucan complex is then trafficked to the Golgi apparatus via endosomes. However, the Dectin-1/glucan complex dissociates after early internalization, followed by glucan colocalizing with Golgi-associated Dectin-1 at later time points. BG, β-glucan.