Fig. 6.
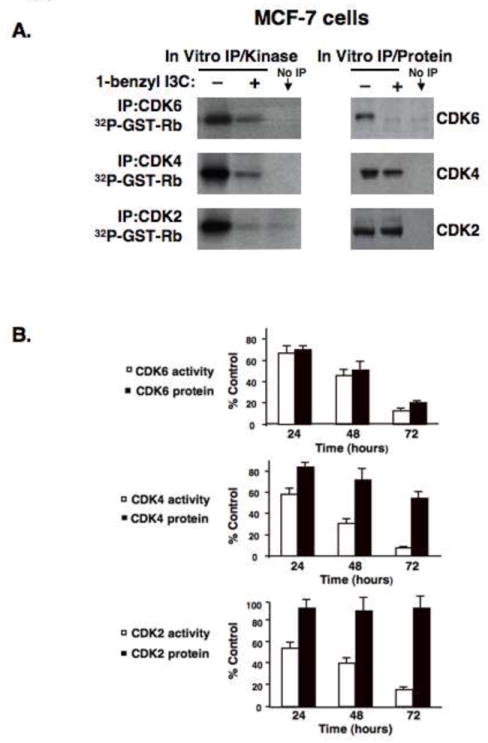
Effects of 1-benzyl-I3C on the specific enzymatic activities of the G1 acting Cyclin Dependent Kinases. (A) MCF-7 cells were treated with either 0.2 μM 1-benzyl-I3C or the DMSO vehicle control for 72 hours followed by immunoprecipitations of CDK2, CDK4, or CDK6 as described in Materials and Methods section. One aliquot of each immunoprecipitation was assayed in vitro for protein kinase activity using GST-Rb as a substrate (left panels), and the other aliquot was used to assess total CDK protein levels in each immunoprecipitation by western blot analysis (right panels). The No IP lane represents an immunoprecipitation with a non-specific IgG. (B) MCF-7 were treated with 0.2 μM 1-benzyl-I3C for indicated times, and at each time point, the enzymatic activities and protein levels of immunoprecipitated CDKs were performed as described above. The amount of immunoprecipitated CDK protein was quantified by densitometry, and the level of [32P]GST-Rb generated from the corresponding kinase assays was determined by phosphoimager analysis as described in Materials and Methods. The values are expressed as percentage of growing control cells not with the vehicle control DMSO at each time point, which was calculated by dividing the values of 1-benzyl-I3C treated cells with the values of vehicle control treated cells. Error bars represent standard error of the mean three independent experiments.
