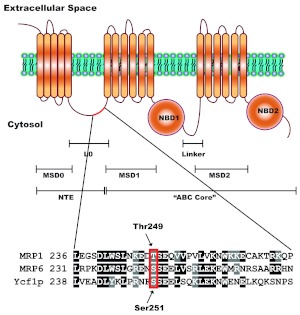
Fig. 1.
A putative CK2 phosphorylation site is semiconserved in human MRP1. The structure of MRP1 consists of a unique for ABCC subfamily NTE and a common ABC “core” region. The NTE is composed of one membrane-spanning domain (MSD0) and a cytosolic linker (L0), whereas the ABC “core” region, common to all ABC proteins, contains two membrane-spanning domains (MSD1 and MSD2) and two nucleotide-binding domains (NBD1 and NBD2). The NTE is thought to be involved in protein trafficking, stability, substrate binding, transport (Bakos et al., 2000; Fernández et al., 2002; Mason and Michaelis, 2002), and possibly in protein dimerization (Doyle et al., 1998; Yang et al., 2007, 2010). The full-length ABCC protein sequences, MRP1, MRP6, and Ycf1p were aligned using ClustalW. Alignment revealed that Ser251 of NTE, recently characterized as Cka1p regulatory site on Ycf1p (Paumi et al., 2008; Pickin et al., 2010) is semiconserved in human MRP1 as Thr249. The site is also conserved in murine MRP6 and was shown to be phosphorylated in vivo (Villén et al., 2007).