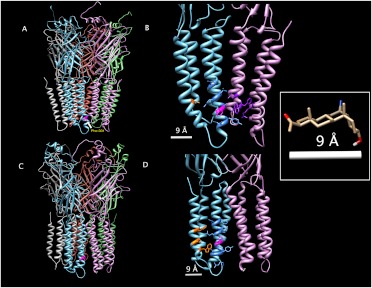
Fig. 7.
Structural modeling of homomeric β3 GABAA receptors. A and C, β3 GABAA receptor models using the Glu-Cl X-ray-determined structure (A) and the nicotinic acetylcholine receptor cryo-electron microscopy-determined structure (C) as templates. B and D, enlarged view of the transmembrane regions of two adjacent subunits, showing candidate 6-AziP-interacting amino acids with Glu-Cl (B) and nicotinic acetylcholine receptor (D) as templates. In all panels, Phe301 on one subunit is colored magenta; in B and D, all 6-AziP-accessible residues within 9 Å of Phe301 are shown in stick form and residues located on TM4 are colored orange, TM3 blue, and TM1 and TM4 of the adjacent subunit purple. Inset, structure of 6-AziP with only polar hydrogens shown. The distance from C6 to the ketone oxygen is 8.42 Å; this distance was rounded to 9 Å and was used to identify the candidate 6-AziP-accessible residues shown in B and D.