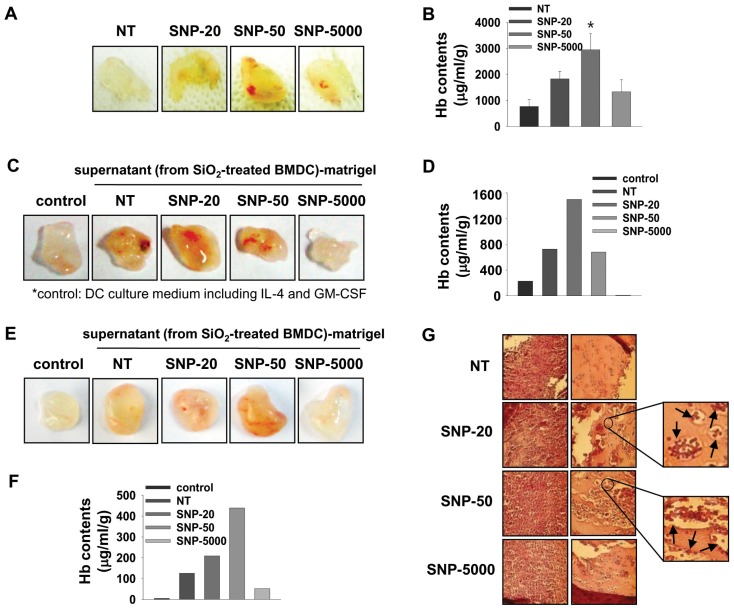
Figure 4.
Silica nanoparticles elicit inflammatory responses in vivo. C57BL/6 mice were injected subcutaneously with 700 µl liquid matrigel containing silica nanoparticles (10 mg/kg). After 10 days, gels were excised (A) and hemoglobin in matrigel plugs was determined using Drabkin's reagent (B). BMDCs were exposed to silica nanoparticles (40 µg/ml) for 24 h (C and D). In addition, bone marrow-derived cells were cultured with 10 ng/ml of GM-CSF, 10 ng/ml of IL-4, and 10 µg/ml of silica nanoparticles for 7 days (E and F). The culture supernatants were collected for last 24 h and concentrated with centricon centrifugal filter devices. A mixture of 500 µl liquid matrigel and 200 µl concentrated supernatant was injected to C57BL/6 mice subcutaneously. After 9~10 days, gels were excised (C and E) and hemoglobin in matrigel plugs was determined (D and F). DC 2.4 cells were treated with silica nanoparticles (40 µg/ml) for 24 h. DC2.4 cells treated with silica nanoparticles were isolated by a density gradient centrifugation on ficoll to remove contamination of silica nanoparticles. C57BL/6 mice were injected subcutaneously with 700 µl liquid matrigel containing 5×105 DC2.4 cells. After 10 days, gels were excised and matrigel plugs were stained with hematoxylin & eosin (H&E) (G). Results represent the mean±SD from duplicates. *p<0.05 for one-way ANOVA.