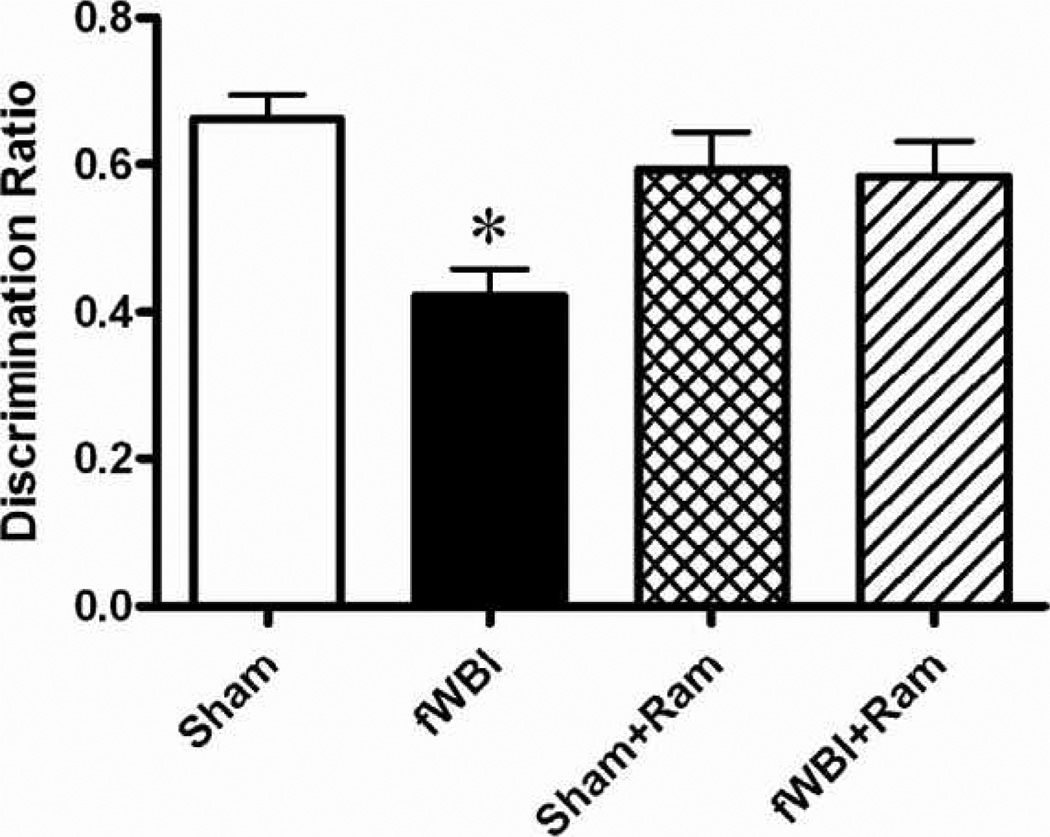
FIG. 1.
Administration of the angiotensin-converting enzyme-inhibitor, ramipril, to young adult male F344 rats before, during, and after fractionated whole-brain irradiation prevents radiation-induced perirhinal-cortex-dependent cognitive impairment measured by the perirhinal-cortex-dependent version of the novel object recognition task. Rats received either sham irradiation (Sham), 40 Gy of fractionated whole-brain irradiation (fWBI), sham irradiation + 15 mg/L of ramipril in the drinking water (Sham + Ram), or 40 Gy of fractionated whole-brain irradiation + ramipril (fWBI + Ram). Ramipril was continuously administered to the rats starting 3 days before the beginning of fractionated whole-brain irradiation. Cognitive function was assessed 26 weeks after completion of fractionated whole-brain irradiation. Data represent the mean ± SEM; n = 20/group; *P < 0.05.