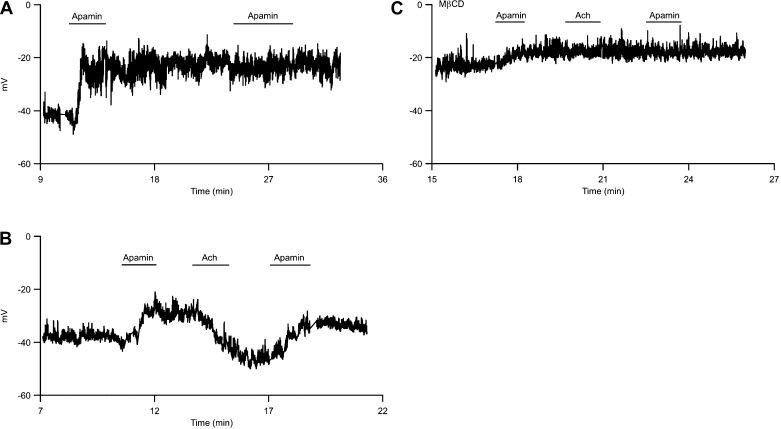
Fig. 6.
Acetylcholine (Ach) reverses apamin-induced depolarization. A: endothelial membrane potential was recorded using whole cell perforated patch in current-clamp mode and was plotted against time of experiment. Time 0 indicates gigaseal formation. Application of apamin in the bath causes membrane depolarization. B: Ach repolarizes apamin-induced depolarization. C: membrane potential recording from an endothelial cell treated with MβCD. Recording chamber is continually perfused with external recording solution. Horizontal bars indicate brief application of apamin or acetylcholine to the bath.