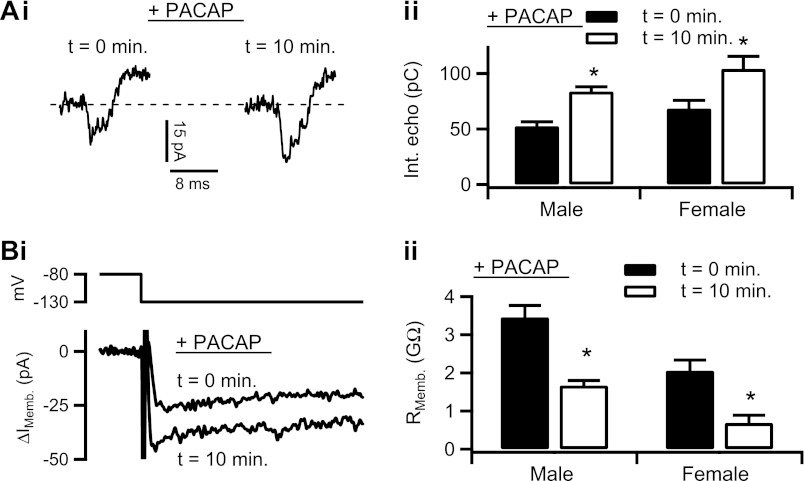
Fig. 4.
PACAP increases electrical coupling. Ai: effect of PACAP stimulation on electrical coupling was tested and a representative recording is provided. Cell was treated with 1 μM PACAP by focal perfusion for 10 min, and the electrical echo protocol was repeated, showing an increase in echo magnitude. Aii: protocol was repeated in male mouse chromaffin cells (n = 21 echoes) and female mouse chromaffin cells (n = 27 echoes). Echo integral data from each PACAP-stimulation time point were separated by gender and plotted as means ± SE. Male: *statistical significance at P = 0.0001; female: *statistical significance at P = 0.011. Bi: input resistance in response to PACAP stimulation was measured, as in Fig. 2 from a chromaffin cell. Representative traces show an increase in inward IMemb after 10 min PACAP treatment at −130 mV, indicating a decreased input resistance. Bii: this protocol was repeated in 15 cells from male mice and in 27 cells from female mice. Input resistance data were separated by gender and treatment condition and plotted as means ± SE. Male: *statistical significance at P = 0.005; female: *statistical significance at P = 0.048.