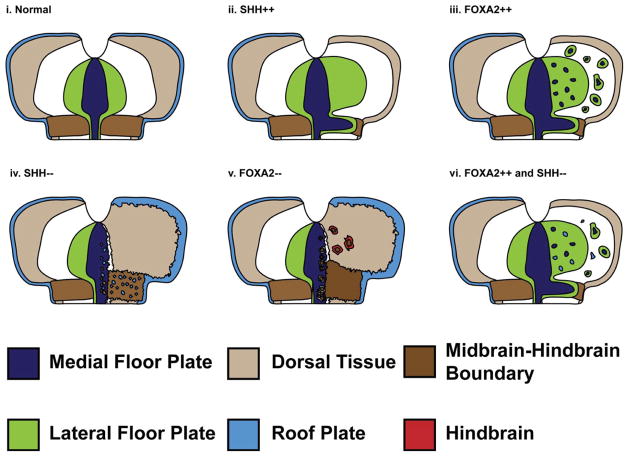
Figure 8. Cartoon summarizing the role of SHH and FOXA2 in patterning the MFP, MHB and RP.
(i) Schematic depicting the normal spatial relationships among the RP (light blue), MFP (dark blue), LFP (green), MHB (dark brown) and dorsal midbrain (beige). (ii) Unilateral SHH misexpression (right side) ectopically induces LFP and can induce MFP along the MHB while concurrently suppressing MHB fates. Dorsal cell fates, including RP are also suppressed. (iii) Unilateral FOXA2 misexpression can ectopically induce MFP along the MHB as well as away from the MHB. (iv) In the absence of HH, the MFP can be converted into the MHB or the RP. (v) The loss of FOXA2 converts the ventral midbrain and the MFP into the MHB. As a consequence of ectopic MHB induction, midbrain fate (OTX2+) is suppressed (not shown) and hindbrain fate (GBX2+, red) is induced. (vi) FOXA2 overexpression combined with HH blockade results in ectopic RP induction throughout ventral midbrain.