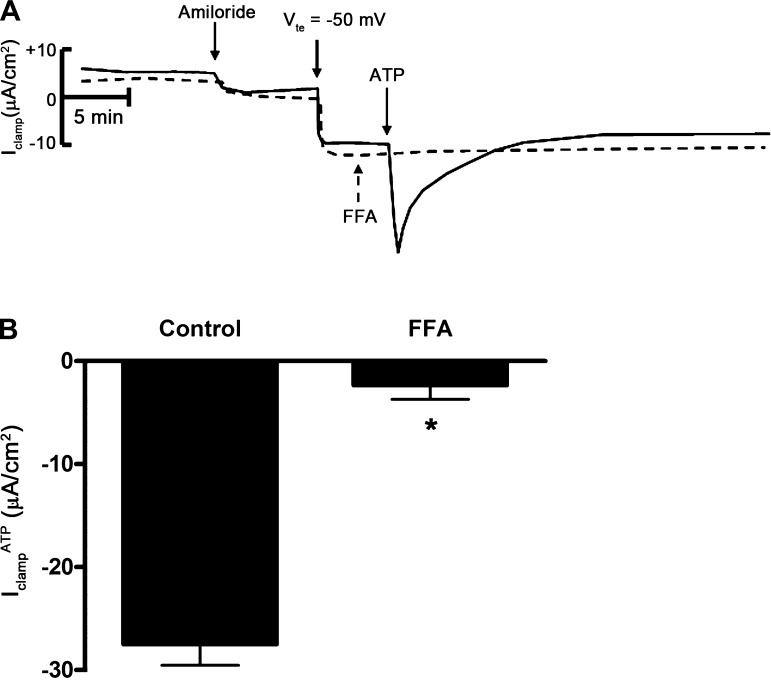
Fig. 7.
Flufenamic acid (FFA) inhibits ATP-inducible clamp current in mpkCCDc14 cells. A: superimposed Iclamp traces of cell monolayers treated with amiloride (10−5 M), clamped to a transepithelial voltage (Vte) of −50 mV, and then treated with vehicle control (solid trace) or FFA (dashed trace). FFA indicates addition of FFA (2 × 10−4 M) to the apical side; ATP indicates addition of ATP (10−6 M ATP) to the apical side. B: quantitation of Iclamp values in response to apical addition of ATP in control filters or in filters pretreated with FFA to the apical side (n = 6 filters). *P < 0.05.