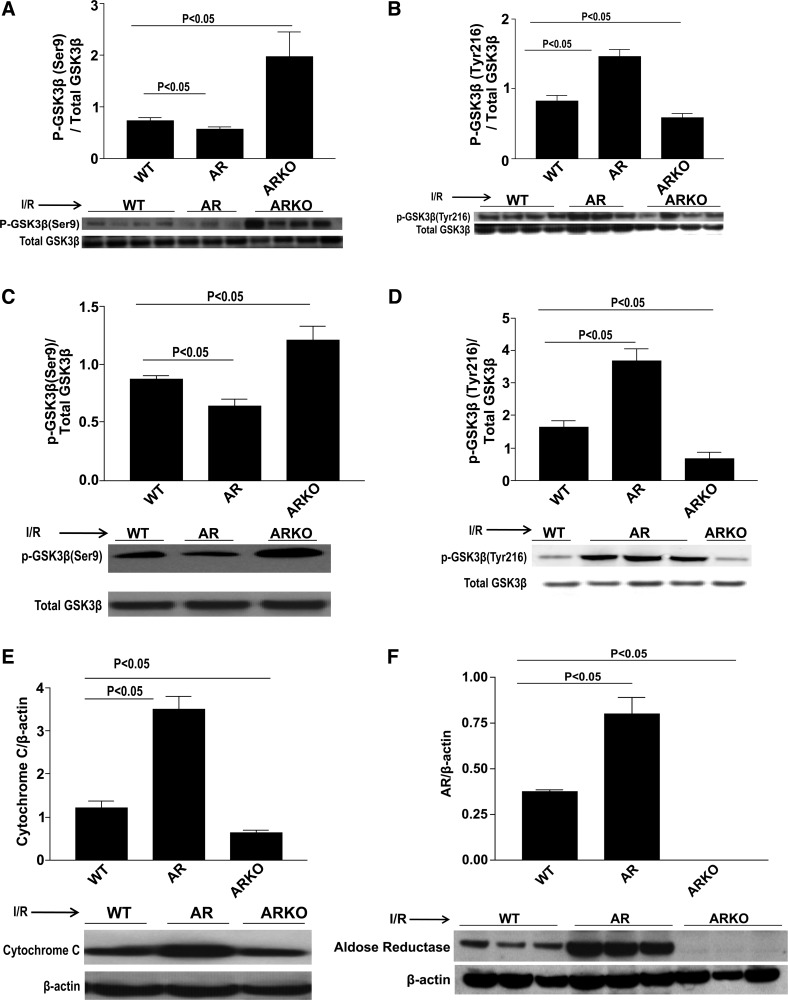
Fig. 1.
Glycogen synthase kinase-3β (GSK3β) phosphorylation expression in wild-type (WT), aldose reductase transgenic (ARTg), and aldose reductase knockout (ARKO) mice. Western blot analysis for phospho (p)-GSK3β-Ser9 [isolated heart (A) and LAD ligation (C)], p-GSK3β-Tyr216 [isolated heart (B) and LAD ligation (D)], cytochrome c (E), and aldose reductase (AR) expression (F) in untreated WT, ARTg, and ARKO mice hearts subjected to ischemia-reperfusion (I/R). ARTg hearts showed decreased p-GSK3β inhibition compared with WT hearts. ARKO hearts had significant increases in p-GSK3β (Ser9) (P < 0.05). ARTg hearts displayed a more than threefold increase in apoptosis compared with WT and ARKO hearts as was measured by cytochrome c expression (P < 0.05). ARKO hearts displayed significant decreases in apoptotic levels compared with WT (P < 0.05). ARTg hearts displayed a twofold increase in AR expression compared with WT (n = 4–16 mice/group).