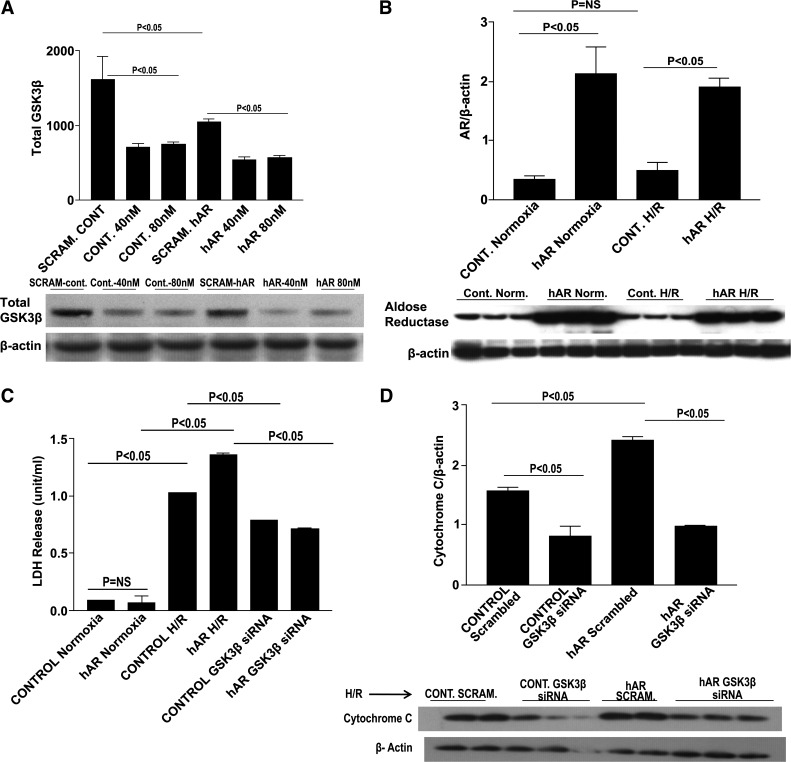
Fig. 5.
GSK3β small-interfering RNA (siRNA) knock down in HL-1 cells. Western blot analysis for total GSK3β dose-dependent siRNA knockdown (A) and AR expression (B). Determination of cardiac injury as determined by LDH release in control and human AR (hAR) siRNA knock down of GSK3β (C). D: Western blot analysis of cytochrome c expression in control and hAR-overexpressing cells transfected with GSK3β siRNA. No change in LDH release was observed in control and hAR-overexpressing cells exposed to 30 min of normoxia alone. Thirty minutes of hypoxia followed by 60 min of reoxygenation increased LDH release (P < 0.05), whereas inhibiting GSK3β with siRNA significantly reduced LDH release and injury (P < 0.05). hAR-transfected cells, as expected, had greater AR expression than control cells. There was no difference in AR expression between HL-1 control cells subjected to normoxic and H/R conditions. GSK3β siRNA knock down significantly reduced GSK3β expression in both control and hAR-overexpressing cells. Inhibition of GSK3β significantly reduced apoptotic levels in both control and hAR-overexpressing cells. NS, not significant. Error bars not visible. Control normoxia: SE ± 0.003; control hAR: SE ± 0.006; control GSK3β siRNA: ±0.005.