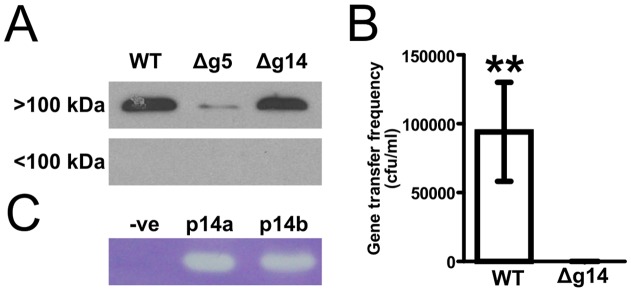
Figure 6. Role of p14 in RcGTA release.
A. Wild type R. capsulatus SB1003 culture supernatant fractions were prepared by size exclusion filtration, and used in western blots probed with RcGTA capsid antiserum. Blots are shown of the fraction containing proteins in excess of 100 kDa (Upper Panel) and that containing proteins less than 100 kDa (Lower Panel). The designation Δg5 indicates the supernatant from a transposon knock-out of RcGTA g5, used as a negative control strain that lacks the capsid protein. B. Gene transfer frequency for SB1003 and SB1003Δg14. Strains were grown anaerobically with illumination to stationary growth phase in YPS. Frequency of gene transfer is the number rifampicin resistant colonies per ml, resulting from infection of a rifampicin-sensitive strain (B10) with RcGTA particles from the rifampicin resistant strains SB1003 or SB1003Δg14. Means were calculated from 3 biological replicates. Error bars show standard deviation. Double asterisks denote a p-value ≤0.01 derived from a one tailed, two sample t-test. C. Peptidoglycan zymogram of two E. coli pET28a-g14 overexpression cultures (p14a/b) and a negative control (−ve) of E. coli lacking the g14 gene. Gels were stained with Coomassie brilliant blue and zones of clearing indicate localized degradation of peptidoglycan.