Figure 5. Increased oxidative stress in ISO stimulated cerebral arteries (ISO-CAs).
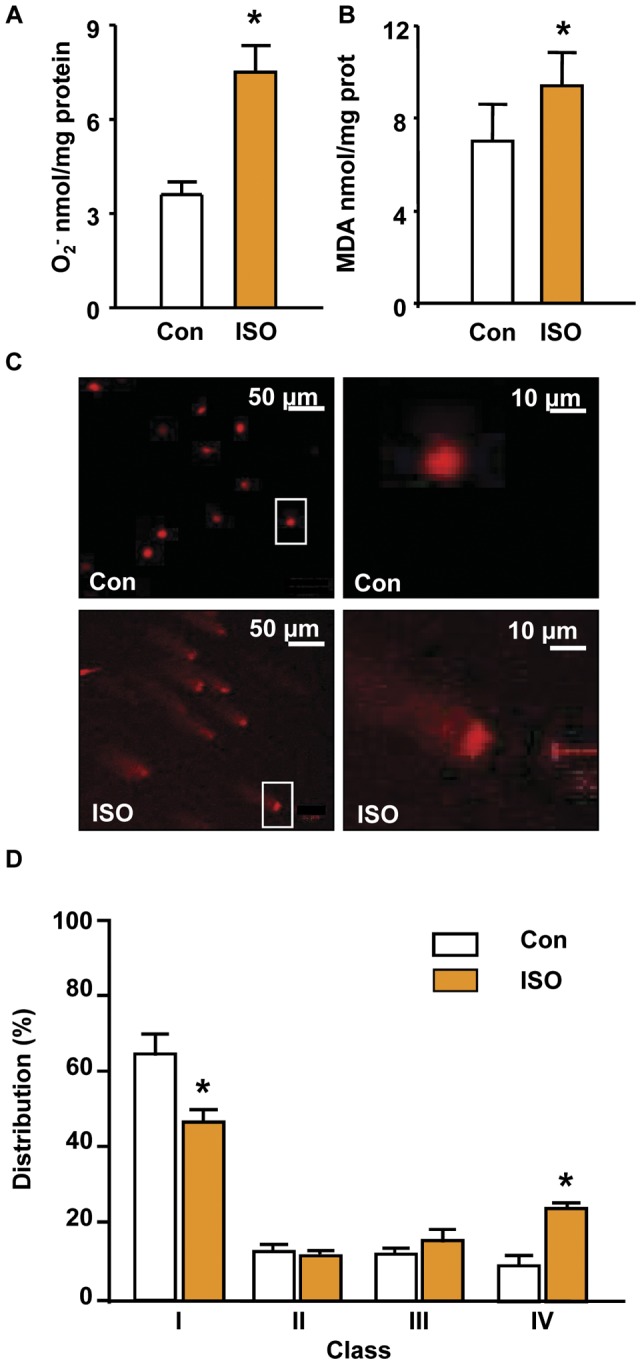
A. NADPH-dependent O2- production was highly increased in ISO-CAs group (7.5±0.85 O2- nmol/mg protein) than control (3.6±0.40; mean ± SEM, Student's t-test, * P<0.05 vs. Con, n = 6). B. ROS-induced lipid oxidation was highly increased in ISO-CAs group. C. Oxidative DNA damage in smooth muscle cells (SMCs) from ISO-CAs was assessed by comet assay. Nuclear DNA was stained with propidium iodide and examined under a confocal laser scanning microscope. More highly damaged DNA was observed in SMCs from ISO-CAs (c, d) compared to the control (a, b) based on tail length. Magnification: 100× for a and c, 500× for b and d. D. Statistical summary obtained from comet image analysis. Less damaged cells, class I, were significantly more common in control (65.1±5.9%) than in ISO- (47.5±3.6%) CAs, whereas severely damaged cells, class IV, were markedly more frequent in ISO-CAs (24.7±1.3%) than in the control (9.5±3.2%; mean ± SEM, Student’s t-test, * P<0.05 vs. Con, n = 4).
