Figure 4. Morphological and functional modifications induced by CD157 knockdown in OV-90 cells.
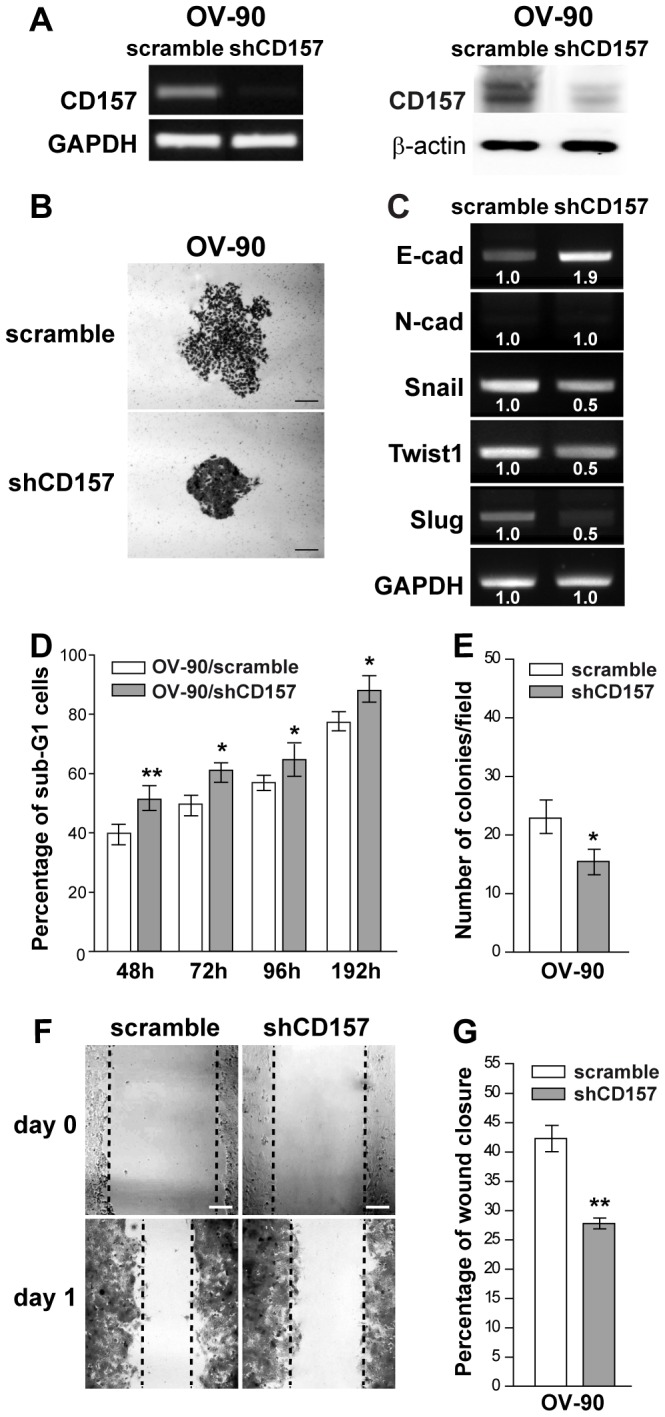
(A) sqRT-PCR (left) and western blot analysis (right) showing OV-90 cells retrovirally transduced with a shRNA that targets the human CD157 mRNA, resulting in efficient knockdown of CD157 expression. GAPDH and β-actin were used as internal controls, respectively. (B) Morphology of colonies formed by OV-90/scramble and OV-90/shCD157 cells. Representative colonies visualized after crystal violet staining are shown. Scale bar: 200 µM. (C) sqRT-PCR for E-cadherin, N-cadherin and Snail, Twist1 and Slug transcriptional repressors in OV-90/scramble and OV-90/shCD157 cells. Densitometry quantifies the levels of mRNA expression of the indicated molecules relative to GAPDH. (D) Anoikis assay. After 48, 72, 96 and 192 h under anchorage-independent growth, cells were fixed, stained with propidium iodide and analyzed with a FACSCanto. Data analysis was performed with ModFit LT™ cell cycle analysis software. Anoikis in OV-90/scramble and OV-90/shCD157 cells was determined by measuring the percent of sub-G1 cells. Results represent the mean ± SEM of three independent experiments. *P<0.05; **P<0.01, two-tailed t test. (E) Anchorage-independent growth of OV-90/scramble and OV-90/shCD157 cells was analyzed by soft agar colony formation assay. Graph represents the average number of colonies/field formed from three independent experiments ± SEM after 3 weeks incubation of cells in soft agar. *P<0.05, two-tailed t test. (F) Effect of CD157 knockdown on OV-90 cell migration in a scratch-wound assay. Cells were grown as monolayers, wounded, and photographed at time 0 and at 24 h (scale bar: 200 µM). Wound edges are indicated by black dashed lines. (G) The ability of OV-90/scramble and OV-90/shCD157 cells to close the wound was calculated by measuring 20 randomly chosen distances along the wound edge at time 0 and at 24 h. Results represent the percentage reduction of the average wound width and are expressed as the mean ± SEM of three independent experiments. **P<0.01, two-tailed t test.
