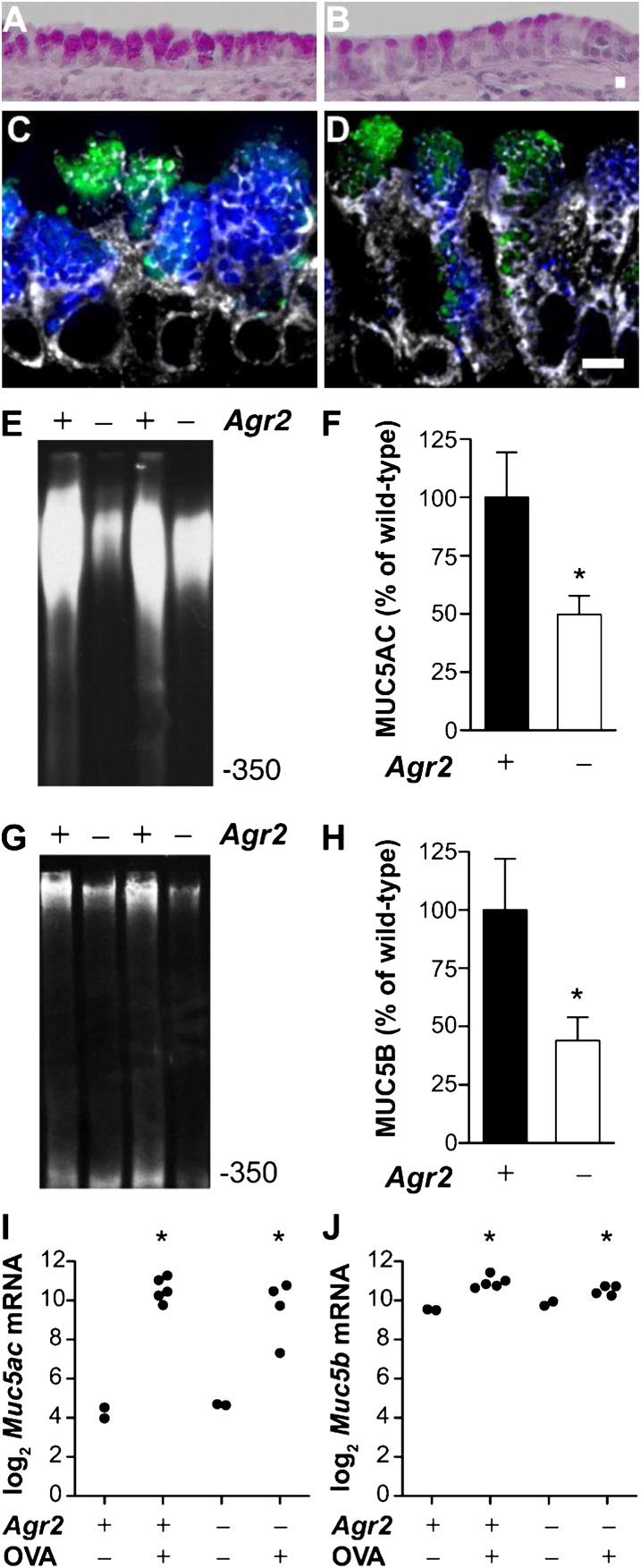
Figure 6.
Mucin is reduced in airway epithelium from allergen-challenged Agr2−/− mice. Periodic acid Schiff staining of airways from allergen-sensitized and -challenged wild-type (A) and Agr2−/− (B) mice. Immunofluorescence staining of airways from allergen-sensitized and -challenged wild-type (C) and Agr2−/− (D) mice with antibodies against MUC5AC (blue) and MUC5B (green) and the ER-marker GRP78/GRP94 (gray). Scale bar: 5 μm. Representative immunoblots and densitometry for MUC5AC (E, F) and MUC5B (G, H) protein from allergen-challenged wild-type control (+) and Agr2−/− (−) mice. Mucin signal (mean ± SEM for ≥ 5 mice per group) is represented as a percentage of the mean signal from allergen-challenged wild-type mice. *P < 0.05 versus allergen-challenged wild-type mice. (I, J) qRT-PCR was used to measure Muc5ac (A) and Muc5b (B) mRNA in epithelial brushings from wild-type and AGR2-deficient mice after saline (OVA−) or allergen (OVA+) challenge. Each point represents data from one mouse. *P < 0.05 versus wild-type saline-challenged mice. Mucin transcript levels in allergen-challenged Agr2−/− and control groups were not significantly different.